Cloning and functional characterization of a novel dopamine receptor from Drosophila melanogaster
- PMID: 8656286
- PMCID: PMC6578617
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.16-12-03925.1996
Cloning and functional characterization of a novel dopamine receptor from Drosophila melanogaster
Abstract
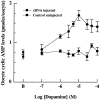
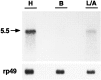
A cDNA clone is described that encodes a novel G-protein-coupled dopamine receptor (DopR99B) expressed in Drosophila heads. The DopR99B receptor maps to 99B3-5, close to the position of the octopamine/tyramine receptor gene at 99A10-B1, suggesting that the two may be related through a gene duplication. Agonist stimulation of DopR99B receptors expressed in Xenopus oocytes increased intracellular Ca2+ levels monitored as changes in an endogenous inward Ca2+-dependent chloride current. In addition to initiating this intracellular Ca2+ signal, stimulation of DopR99B increased cAMP levels. The rank order of potency of agonists in stimulating the chloride current is: dopamine > norepinephrine > epinephrine > tyramine. Octopamine and 5-hydroxytryptamine are not active (< 100 microM). This pharmacological profile plus the second-messenger coupling pattern suggest that the DopR99B receptor is a D1-like dopamine receptor. However, the hydrophobic core region of the DopR99B receptor shows almost equal amino acid sequence identity (40-48%) with vertebrate serotonergic, alpha 1- and beta-adrenergic, and D1-like and D2-like dopaminergic receptors. Thus, this Drosophila receptor defines a novel structural class of dopamine receptors. Because DopR99B is the second dopamine receptor cloned from Drosophila, this work establishes dopamine receptor diversity in a system amenable to genetic dissection.
Figures




References
-
- Ali DW, Orchard I. Characterization of dopamine and serotonin receptors on the salivary glands of the locust, Locusta migratoria . Biog Amines. 1994;10:195–212.
-
- Arakawa S, Gocayne JD, McCombie WR, Urquhart DA, Hall LM, Fraser CM, Venter JC. Cloning, localization, and permanent expression of a Drosophila octopamine receptor. Neuron. 1990;4:343–354. - PubMed
-
- Barnard EA, Miledi R, Sumikawa K. Translation of exogenous messenger RNA coding for nicotinic acetylcholine receptors produces functional receptors in Xenopus oocytes. Proc R Soc Lond [Biol] 1982;215:241–246. - PubMed
-
- Bodnaryk RP. Identification of specific dopamine- and octopamine-sensitive adenylate cyclases in the brain of Mamestra configurata Wlk. Insect Biochem. 1979;9:155–162. - PubMed
-
- Brown CS, Nestler C. Catecholamines and indolalkylamines. In: Kerkut GA, Gilbert LI, editors. Comprehensive insect physiology, biochemistry and pharmacology, Vol. 11. Pergamon; Oxford: 1985. pp. 436–497.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
