Biosynthesis of an endogenous cannabinoid precursor in neurons and its control by calcium and cAMP
- PMID: 8656287
- PMCID: PMC6578613
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.16-12-03934.1996
Biosynthesis of an endogenous cannabinoid precursor in neurons and its control by calcium and cAMP
Abstract
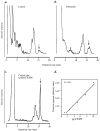
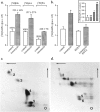
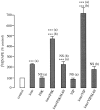
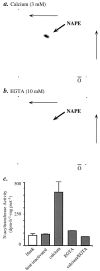
Understanding the mechanisms involved in the biogenesis of N-arachidonoylethanolamine (anandamide) and N-palmitoylethanolamine is important in view of the possible role of these lipids as endogenous cannabinoid substances. Anandamide (which activates cannabinoid CB1 receptors) and N-palmitoylethanolamine (which activates a CB2-like receptor subtype in mast cells) may both derive from cleavage of precursor phospholipid, N-acylphosphatidylethanolamine (NAPE), catalyzed by Ca(2+)-activated D-type phosphodiesterase activity. We report here that the de novo biosynthesis of NAPE is enhanced in a Ca(2+)-dependent manner when rat cortical neurons are stimulated with the Ca(2+)-ionophore ionomycin or with membrane-depolarizing agents such as veratridine and kainate. This reaction is likely to be mediated by a neuronal N-acyltransferase activity, which catalyzes the transfer of an acyl group from phosphatidylcholine to the ethanolamine moiety of phosphatidylethanolamine. In addition, we show that Ca2+-dependent NAPE biosynthesis is potentiated by agents that increase cAMP levels, including forskolin and vasoactive intestinal peptide. Our results thus indicate that NAPE levels in cortical neurons are controlled by Ca2+ ions and cAMP. Such regulatory effect may participate in maintaining a supply of cannabimimetic N-acylethanolamines during synaptic activity, and prime target neurons for release of these bioactive lipids.
Figures


References
-
- Cadas H, Schinelli S, Piomelli D (1996) Membrane localization of N-acylphosphatidylethanolamine in central neurons: studies with exogenous phospholipases. J Lipid Med, in press. - PubMed
-
- Colodzin M, Bachur N, Weissbach H, Udenfriend S. Enzymatic formation of fatty acid amides of ethanolamine by rat liver microsomes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1963;10:165–170. - PubMed
-
- Christie W. Pergamon; Oxford: 1987. HPLC and lipids: a practical guide, pp 23–25. .
-
- Desarnaud F, Cadas H, Piomelli D. Anandamide amidohydrolase activity in rat brain microsomes: identification and partial characterisation. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:6030–6035. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
