Visual stimulation regulates the expression of transcription factors and modulates the composition of AP-1 in visual cortex
- PMID: 8656291
- PMCID: PMC6578611
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.16-12-03968.1996
Visual stimulation regulates the expression of transcription factors and modulates the composition of AP-1 in visual cortex
Abstract
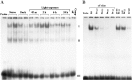
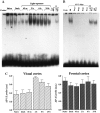
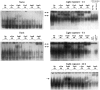
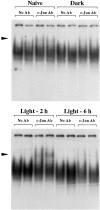
It is believed that long-term changes in neuronal function are orchestrated by transcription factors, such as AP-1 and ZIF 268, which are in turn regulated by synaptic stimulation. To further our understanding of the functional effects of such expression, we have examined the DNA-binding activities of both AP-1 and ZIF 268 by way of electrophoretic mobility shift assays (EMSA) on nuclear extracts from visual cortices of rats treated with selective light exposure. Visual stimulation after dark rearing increased the DNA-binding activities of both AP-1 and ZIF 268 to their highest levels within 2 hr. ZIF 268 thereafter dropped to levels similar to that observed in naive animals, whereas AP-1 DNA-binding activity continued to remain elevated even after 24 hr of stimulation. The components of the AP-1 complex, when assessed by EMSA-supershift analysis, showed considerable variability under different conditions of exposure. FosB and JunD were the major constituents of AP-1 in both naive and dark-reared animals. Brief visual stimulation (2 hr) added c-Fos, c-Jun, and JunB to this complex, whereas prolonged stimulation (6-24 hr) reduced c-Fos and c-Jun levels significantly, leaving only FosB, JunB, and JunD as the major components of AP-1. These results suggest that transcriptional control by AP-1 may be generated by selective combinatorial interactions of different members of the Fos and Jun families and that are guided by activity-dependent processes.
Figures




References
-
- Angel P, Karin M. The role of Jun, Fos and the AP-1 complex in cell-proliferation and transformation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991;1072:129–157. - PubMed
-
- Beaver CJ, Mitchell DE, Robertson HA. An immunohistochemical study of the rapid pattern of expression of c-Fos protein in the visual cortex of dark-reared kittens following initial exposure to light. J Comp Neurol. 1993;333:469–484. - PubMed
-
- Benson DL, Huntsman MM, Jones EG. Activity dependent changes in GAD and preprotachykinin mRNAs in visual cortex of adult monkeys. Cereb Cortex. 1994;4:40–51. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
