Undetectable interleukin (IL)-10 and persistent IL-8 expression early in hyaline membrane disease: a possible developmental basis for the predisposition to chronic lung inflammation in preterm newborns
- PMID: 8725256
- PMCID: PMC7101752
- DOI: 10.1203/00006450-199606000-00007
Undetectable interleukin (IL)-10 and persistent IL-8 expression early in hyaline membrane disease: a possible developmental basis for the predisposition to chronic lung inflammation in preterm newborns
Abstract
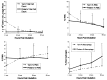
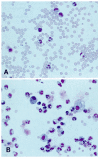
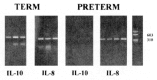
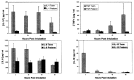
We are interested in determining whether premature birth alters expression of counterregulatory cytokines which modulate lung inflammation. Production of proinflammatory cytokines tumor necrosis factor alpha. IL-1 beta, and IL-8 is regulated in part by the antiinflammatory cytokine IL-10. For preterm newborns with hyaline membrane disease, deficiencies in the ability of lung macrophages to express antiinflammatory cytokines may predispose to chronic lung inflammation. We compared the expression of pro- and antiinflammatory cytokines at the mRNA and protein level in the lungs of preterm and term newborns with acute respiratory failure from hyaline membrane disease or meconium aspiration syndrome. Four sequential bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) samples were obtained during the first 96 h of life from all patients. All patients rapidly developed an influx of neutrophils and macrophages. Over time, cell populations in both groups became relatively enriched with macrophages. The expression of proinflammatory cytokine mRNA and/or protein was present in all samples from both patient groups. In contrast, IL-10 mRNA was undetectable in most of the cell samples from preterm infants and present in the majority of cell samples from term infants. IL-10 concentrations were undetectable in lavage fluid from preterm infants with higher levels in a few of the BAL samples from term infants. These studies demonstrate that 1) IL-10 mRNA and protein expression by lung inflammatory cells is related to gestational age and 2) during the first 96 h of life neutrophil cell counts and IL-8 expression decrease in BAL from term infants, but remain unchanged in BAL samples from preterm infants.
Figures

References
-
- deLemos RA, Yoder B, McCurnin D, Kinsella J, Clark R, Null D. The use of high-frequency oscillatory ventilation (HFOV) and extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) in the management of the term/near term infant with respiratory failure. Early Hum Dev. 1992;29:299–303. doi: 10.1016/0378-3782(92)90181-F. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Minoo P, Segura L, deLemos R, Coalson JJ, King RJ. Alterations in surfactant protein gene expression associated with premature birth and exposure to hyperoxia. Am J Physiol. 1991;261:L386–L392. - PubMed
-
- Ogden BE, Murphy S, Saunders GC, Johnson JD. Lung lavage of newborns with respiratory distress syndrome: prolonged neutrophil influx is associated with bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Chest. 1983;83:31–33. - PubMed
-
- Bonikos DS, Bensch KG, Merit TA. Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia. 1988. pp. 33–58.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

