gp120-induced neurotoxicity in hippocampal pyramidal neuron cultures: protective action of TGF-beta1
- PMID: 8753870
- PMCID: PMC2689548
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.16-13-04080.1996
gp120-induced neurotoxicity in hippocampal pyramidal neuron cultures: protective action of TGF-beta1
Abstract
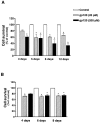
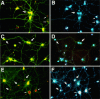
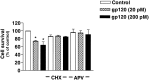
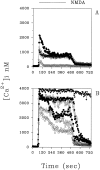
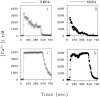
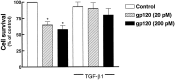
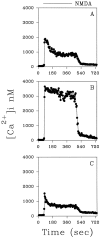
We found that TGF-beta1, a cytokine that previously has been reported to have neuroprotective effects, was able to prevent the toxicity induced by the HIV-1 coat protein gp120 in hippocampal pyramidal neuron cultures. In the presence of glia, gp120 induced time- and dose-dependent cell death, which was more pronounced in mature (7-19 d in culture) than in young neurons (2-7 d in culture). Staining with nuclear dyes (propidium iodide and Hoechst 33342), in situ detection of DNA fragments, and DNA analysis on agarose gels indicated that apoptosis was mainly responsible for the death caused by the viral protein. However, after several days of treatment, death-displaying necrotic features also occurred. Neurotoxicity induced by gp120 was dependent on the activation of NMDA receptors and required the presence of glia as well as new protein synthesis. Thus, the effect of gp120 was abolished by the NMDA receptor antagonist APV and partially reduced by cycloheximide. Only modest neurotoxicity was observed in pure neuronal cultures deprived of the glia feeder layer. Fura-2-based videoimaging showed that treatment with gp120 enhanced the ability of NMDA to increase neuronal [Ca2+]i. The impairment of neuronal Ca2+ homeostasis was prevented completely by TGF-beta1. Therefore, it is likely that the neuroprotective action of the cytokine is attributable to its ability to stabilize neuronal [Ca2+]i.
Figures


References
-
- Abele AE, Scholz KP, Scholz WK, Miller RJ. Excitotoxicity induced by enhanced excitatory neurotransmission in cultured hippocampal pyramidal neurons. Neuron. 1990;2:413–419. - PubMed
-
- Apostolski S, McAlarney T, Quattrini A. The gp120 glycoprotein of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 binds to sensory ganglion neurons. Ann Neurol. 1993;34:855–863. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
