Ultrastructural immunocytochemical localization of mu-opioid receptors in rat nucleus accumbens: extrasynaptic plasmalemmal distribution and association with Leu5-enkephalin
- PMID: 8753878
- PMCID: PMC6579005
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.16-13-04162.1996
Ultrastructural immunocytochemical localization of mu-opioid receptors in rat nucleus accumbens: extrasynaptic plasmalemmal distribution and association with Leu5-enkephalin
Abstract
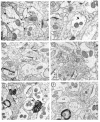
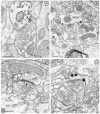
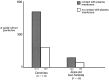
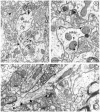
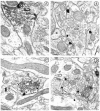
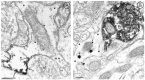
mu-Opioid receptors and their endogenous ligands, including Leu5-enkephalin (LE), are distributed abundantly in the nucleus accumbens (NAC), a region implicated in mechanisms of opiate reinforcement. We used immunoperoxidase and/or immunogold-silver methods to define ultrastructural sites for functions ascribed to mu-opioid receptors and potential sites for activation by LE in the NAC. An antipeptide antibody raised against an 18 amino acid sequence of the cloned mu-opioid receptor (MOR) C terminus showed that MOR-like immunoreactivity (MOR-LI) was localized predominantly to extrasynaptic sites along neuronal plasma membranes. The majority of neuronal profiles containing MOR-LI were dendrites and dendritic spines. The dendritic plasma membranes immunolabeled for MOR were near sites of synaptic input from LE-labeled terminals and other unlabeled terminals forming either inhibitory or excitatory type synapses. Unmyelinated axons and axon terminals were also intensely but less frequently immunoreactive for MOR. Observed sites for potential axonal associations with LE included coexistence of MOR and LE within the same terminal, as well as close appositions between differentially labeled axons. Astrocytic processes rarely contained detectable MOR-LI, but also were sometimes observed in apposition to LE-labeled terminals. We conclude that in the rat NAC, MOR is localized prominently to extrasynaptic neuronal and more rarely to glial plasma membranes that are readily accessible to released LE and possibly other opioid peptides and opiate drugs. The close affiliation of MOR with spines receiving excitatory synapses and dendrites receiving inhibitory synapses provides the first direct morphological evidence that MOR selectively modulates postsynaptic responses to cortical and other afferents.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Ultrastructural immunocytochemical localization of mu opioid receptors and Leu5-enkephalin in the patch compartment of the rat caudate-putamen nucleus.J Comp Neurol. 1996 Nov 25;375(4):659-74. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-9861(19961125)375:4<659::AID-CNE7>3.0.CO;2-0. J Comp Neurol. 1996. PMID: 8930791
-
Immunolabeling of Mu opioid receptors in the rat nucleus of the solitary tract: extrasynaptic plasmalemmal localization and association with Leu5-enkephalin.J Comp Neurol. 1996 Aug 5;371(4):522-36. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-9861(19960805)371:4<522::AID-CNE3>3.0.CO;2-6. J Comp Neurol. 1996. PMID: 8841907
-
Ultrastructural localization of mu-opioid receptors in the superficial layers of the rat cervical spinal cord: extrasynaptic localization and proximity to Leu5-enkephalin.Brain Res. 1996 Aug 26;731(1-2):141-54. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(96)00492-1. Brain Res. 1996. PMID: 8883864
-
mu-Opioid receptors are localized to extrasynaptic plasma membranes of GABAergic neurons and their targets in the rat nucleus accumbens.J Neurosci. 1997 Apr 1;17(7):2585-94. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.17-07-02585.1997. J Neurosci. 1997. PMID: 9065518 Free PMC article.
-
Cholinergic axon terminals in the ventral tegmental area target a subpopulation of neurons expressing low levels of the dopamine transporter.J Comp Neurol. 1999 Jul 26;410(2):197-210. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1096-9861(19990726)410:2<197::aid-cne3>3.0.co;2-d. J Comp Neurol. 1999. PMID: 10414527 Review.
Cited by
-
Antidepressant-like and anxiolytic-like effects following activation of the μ-δ opioid receptor heteromer in the nucleus accumbens.Mol Psychiatry. 2014 Sep;19(9):986-94. doi: 10.1038/mp.2013.115. Epub 2013 Sep 24. Mol Psychiatry. 2014. PMID: 24061495
-
The anatomy of co-morbid neuropsychiatric disorders based on cortico-limbic synaptic interactions.Neurotox Res. 2006 Oct;10(2):65-85. doi: 10.1007/BF03033236. Neurotox Res. 2006. PMID: 17062369 Review.
-
Potential of Glial Cell Modulators in the Management of Substance Use Disorders.CNS Drugs. 2020 Jul;34(7):697-722. doi: 10.1007/s40263-020-00721-9. CNS Drugs. 2020. PMID: 32246400 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In situ hybridization histochemical and immunohistochemical evidence that striatal projection neurons co-containing substance P and enkephalin are overrepresented in the striosomal compartment of striatum in rats.Neurosci Lett. 2007 Oct 2;425(3):195-9. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2007.08.033. Epub 2007 Aug 22. Neurosci Lett. 2007. PMID: 17868995 Free PMC article.
-
The role of enkephalinergic systems in substance use disorders.Front Syst Neurosci. 2022 Aug 5;16:932546. doi: 10.3389/fnsys.2022.932546. eCollection 2022. Front Syst Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35993087 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aoki C, Pickel VM. C-Terminal tail of β-adrenergic receptors: immunocytochemical localization within astrocytes and their relation to catecholaminergic neurons in N. tractus solitarii and area postrema. Brain Res. 1992;571:35–49. - PubMed
-
- Beauvillain JC, Moyse E, Dutreiz I, Mitchell V, Poulain P, Mazzuca M. Localization of mu opioid receptors on the membranes of nerve endings and tanycytes in the guinea-pig median eminence by electron microscopic radioautography. Neuroscience. 1992;49:925–936. - PubMed
-
- Broadwell RD, Cataldo AM. The neuronal endoplasmic reticulum: its cytochemistry and contribution to the endomembrane system. J Histochem Cytochem. 1983;31:1077–1088. - PubMed
-
- Browning ET, Ruina M. Glial fibrillary acidic protein: norepinephrine stimulated phosphorylation in intact C-6 glioma cells. J Neurochem. 1984;42:718–726. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
