Dopaminergic regulation of progesterone receptors: brain D5 dopamine receptors mediate induction of lordosis by D1-like agonists in rats
- PMID: 8756415
- PMCID: PMC6579300
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.16-16-04823.1996
Dopaminergic regulation of progesterone receptors: brain D5 dopamine receptors mediate induction of lordosis by D1-like agonists in rats
Abstract
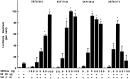
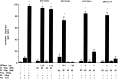
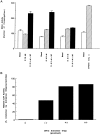
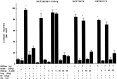
To characterize the signaling pathway by which the neurotransmitter dopamine modulates progesterone receptor (PR) activation, the steroid-dependent behavior lordosis was used in estrogen-primed ovariectomized Sprague-Dawley rats with stereotaxic implanted third ventricle cannulas. Lordosis was observed in response to solicitous males in females after central administration of the D1-like agonist SKF38393 and three of its analogs (SKF77434, SKF75640, and SKF85174). In contrast, D1-like antagonist SCH23390 and D1-like/D2 repopulation inhibitor EEDQ blocked behavior inducible by the D1-like agonists. Further, antisense oligonucleotides to D5, but not D1, dopamine receptor mRNA suppressed reproductive behavior associated with D1-like stimulation. This finding provides strong evidence that dopaminergic modulation of lordosis is mediated by the novel D5 dopamine receptor. Although D1, but not D5, dopamine receptor mRNAs were detected in the ventromedial nucleus (VMN) by in situ hybridization, agonists microinjected into the VMN, but not into the arcuate nucleus or preoptic area, induced lordosis, suggesting the functional presence of D5 dopamine receptors in the VMN. Also in support, D5 receptor mRNA antisense microinjected into the VMN blocked the subsequent induction of lordosis by D1-like agonists. Finally, facilitation of sex behavior by D1-like agonists was blocked by the antiprogestin RU38486 and PR antisense oligonucleotide. Collectively, the data provide strong evidence for dopaminergic modulation of reproductive behavior through D5 dopamine receptor-mediated modulation of PR-dependent behavior in rat CNS.
Figures


Similar articles
-
In vivo regulation of central nervous system progesterone receptors: cocaine induces steroid-dependent behavior through dopamine transporter modulation of D5 receptors in rats.Mol Endocrinol. 1996 Dec;10(12):1595-604. doi: 10.1210/mend.10.12.8961269. Mol Endocrinol. 1996. PMID: 8961269
-
GABA(A), D1, and D5, but not progestin receptor, antagonist and anti-sense oligonucleotide infusions to the ventral tegmental area of cycling rats and hamsters attenuate lordosis.Behav Brain Res. 1999 Aug;103(1):23-34. doi: 10.1016/s0166-4328(99)00020-0. Behav Brain Res. 1999. PMID: 10475161
-
Distribution of D(5) dopamine receptor mRNA in rat ventromedial hypothalamic nucleus.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1999 Dec 20;266(2):556-9. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1999.1851. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1999. PMID: 10600540
-
The physiology, signaling, and pharmacology of dopamine receptors.Pharmacol Rev. 2011 Mar;63(1):182-217. doi: 10.1124/pr.110.002642. Epub 2011 Feb 8. Pharmacol Rev. 2011. PMID: 21303898 Review.
-
Dopamine D1 receptors, regulation of gene expression in the brain, and neurodegeneration.CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2010 Nov;9(5):526-38. doi: 10.2174/187152710793361496. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2010. PMID: 20632973 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Mating-related stimulation induces phosphorylation of dopamine- and cyclic AMP-regulated phosphoprotein-32 in progestin receptor-containing areas in the female rat brain.J Neurosci. 1998 Dec 1;18(23):10189-95. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.18-23-10189.1998. J Neurosci. 1998. PMID: 9822772 Free PMC article.
-
Mice lacking D5 dopamine receptors have increased sympathetic tone and are hypertensive.J Neurosci. 2002 Dec 15;22(24):10801-10. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-24-10801.2002. J Neurosci. 2002. PMID: 12486173 Free PMC article.
-
Associations Between Environmental Resources and the "Wanting" and "Liking" of Male Song in Female Songbirds.Integr Comp Biol. 2017 Oct 1;57(4):835-845. doi: 10.1093/icb/icx117. Integr Comp Biol. 2017. PMID: 28985327 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Minireview: Tipping the balance: ligand-independent activation of steroid receptors.Mol Endocrinol. 2015 Mar;29(3):349-63. doi: 10.1210/me.2014-1315. Epub 2015 Jan 27. Mol Endocrinol. 2015. PMID: 25625619 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibition of 5α-reductase attenuates behavioral effects of D1-, but not D2-like receptor agonists in C57BL/6 mice.Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2013 Apr;38(4):542-51. doi: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2012.07.014. Epub 2012 Aug 9. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2013. PMID: 22877998 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Andersen PH, Jansen JA. Dopamine receptor agonists: selectivity and dopamine D1 receptor efficacy. Eur J Pharmacol Mol Pharmacol Sect. 1990;188:335–347. - PubMed
-
- Cauteras NS, Simerly RB, Swanson LW. Organization of projections from the ventromedial nucleus of the hypothalamus: a phaseolus vulgaris -Leucoagglutinin study in the rat. J Comp Neurol. 1994;348:41–79. - PubMed
-
- Cohen JS. Oligodeoxyribonucleotides. Antisense inhibitors of gene expression. In: Cohen JS, editor. Topics in molecular and structural biology, Vol. 12. Macmillan; London: 1989. pp. 1–215.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
