Reduction of calcium currents by Lambert-Eaton syndrome sera: motoneurons are preferentially affected, and L-type currents are spared
- PMID: 8756422
- PMCID: PMC6579308
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.16-16-04903.1996
Reduction of calcium currents by Lambert-Eaton syndrome sera: motoneurons are preferentially affected, and L-type currents are spared
Abstract
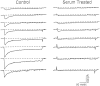
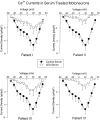
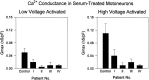
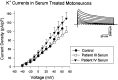
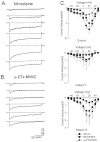
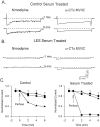
Previous work has demonstrated that Lambert-Eaton syndrome (LES) antibodies reduce calcium currents in nonneuronal cells and neurons and reduce the amplitude of extracellularly recorded currents at mouse motor nerve terminals. We compared effects of LES sera on whole-cell currents of cultured nerve and muscle. LES sera more strongly reduced calcium currents in motoneurons than in sensory neurons. Motoneuronal potassium currents were unaffected. The sera minimally affected calcium currents in skeletal and cardiac muscle. In motoneurons, both low voltage-activated (LVA) and high voltage-activated (HVA) components of calcium current were decreased, demonstrating that the sera targeted more than one calcium channel type. The HVA current remaining in LES-treated motoneurons was little affected by micromolar omega-conotoxin MVIIC but was reduced > 70% by micromolar nimodipine. This pharmacological profile contrasts with untreated cells and suggest that LES sera primarily spare L-type currents in motoneurons.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Passive transfer of Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome induces dihydropyridine sensitivity of ICa in mouse motor nerve terminals.J Neurophysiol. 1998 Sep;80(3):1056-69. doi: 10.1152/jn.1998.80.3.1056. J Neurophysiol. 1998. PMID: 9744921
-
Decreased calcium currents in motor nerve terminals of mice with Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome.J Physiol. 1995 Aug 15;487(1):115-23. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1995.sp020865. J Physiol. 1995. PMID: 7473242 Free PMC article.
-
Lambert-Eaton sera reduce low-voltage and high-voltage activated Ca2+ currents in murine dorsal root ganglion neurons.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 Aug 20;93(17):9264-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.17.9264. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996. PMID: 8799189 Free PMC article.
-
Calcium channel subtypes in lamprey sensory and motor neurons.J Neurophysiol. 1997 Sep;78(3):1334-40. doi: 10.1152/jn.1997.78.3.1334. J Neurophysiol. 1997. PMID: 9310424
-
[Molecular immunology of voltage-gated calcium channel and Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome].Nihon Rinsho. 1997 Dec;55(12):3322-30. Nihon Rinsho. 1997. PMID: 9436458 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Passive transfer of Lambert-Eaton syndrome to mice induces dihydropyridine sensitivity of neuromuscular transmission.J Physiol. 2002 Sep 1;543(Pt 2):567-76. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2002.021048. J Physiol. 2002. PMID: 12205190 Free PMC article.
-
The sodium channel Scn8a is the major contributor to the postnatal developmental increase of sodium current density in spinal motoneurons.J Neurosci. 1998 Jul 15;18(14):5234-9. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.18-14-05234.1998. J Neurosci. 1998. PMID: 9651206 Free PMC article.
-
A mutation in CaV2.1 linked to a severe neurodevelopmental disorder impairs channel gating.J Gen Physiol. 2019 Jun 3;151(6):850-859. doi: 10.1085/jgp.201812237. Epub 2019 Apr 23. J Gen Physiol. 2019. PMID: 31015257 Free PMC article.
-
Zebrafish as a Model System for the Study of Severe CaV2.1 (α1A) Channelopathies.Front Mol Neurosci. 2020 Feb 7;12:329. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2019.00329. eCollection 2019. Front Mol Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32116539 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lambert-Eaton antibodies inhibit Ca2+ currents but paradoxically increase exocytosis during stimulus trains in bovine adrenal chromaffin cells.J Neurosci. 1999 May 1;19(9):3384-95. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.19-09-03384.1999. J Neurosci. 1999. PMID: 10212298 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anderson HJ, Churchill-Davidson HC, Richardson AT. Bronchial neoplasm with myasthenia: prolonged apnea after administration of succinylcholine. Lancet. 1953;2:1291–1293. - PubMed
-
- Bean BP. Classes of calcium channels in vertebrate cells. Annu Rev Physiol. 1989;51:367–384. - PubMed
-
- Blandino JK, Kim YI. Lambert–Eaton syndrome IgG inhibits dihydropyridine-sensitive, slowly inactivating calcium channels in bovine adrenal chromaffin cells. Ann NY Acad Sci. 1993;681:394–397. - PubMed
-
- Bowersox SS, Miljanich GP, Sugiura Y, Li C, Nadasdi L, Hoffman BB, Ramachandran J, Ko CP. Differential blockade of voltage-sensitive calcium channels at the mouse neuromuscular junction by novel ω-conopeptides and ω-agatoxin IVA. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1995;273:248–256. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
