Distinct properties of neuronal and astrocytic endopeptidase 3.4.24.16: a study on differentiation, subcellular distribution, and secretion processes
- PMID: 8756435
- PMCID: PMC6579318
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.16-16-05049.1996
Distinct properties of neuronal and astrocytic endopeptidase 3.4.24.16: a study on differentiation, subcellular distribution, and secretion processes
Abstract
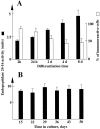
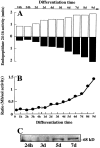
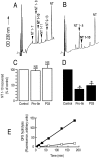
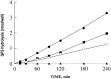
Endopeptidase 3.4.24.16 belongs to the zinc-containing metalloprotease family and likely participates in the physiological inactivation of neurotensin. The peptidase displays distinct features in pure primary cultured neurons and astrocytes. Neuronal maturation leads to a decrease in the proportion of endopeptidase 3.4.24.16-bearing neurons and to a concomitant increase in endopeptidase 3.4.24.16 activity and mRNA content. By contrast, there is no change with time in endopeptidase 3.4.24.16 activity or content in astrocytes. Primary cultured neurons exhibit both soluble and membrane-associated endopeptidase 3.4.24.16 activity. The latter behaves as an ectopeptidase on intact plated neurons and resists treatments with 0.2% digitonin and Na2CO3. Further evidence for an association of the enzyme with plasma membranes was provided by cryoprotection experiments and electron microscopic analysis. The membrane-associated form of endopeptidase 3.4.24.16 increased during neuronal differentiation and appears to be mainly responsible for the overall augmentation of endopeptidase 3.4.24.16 activity observed during neuronal maturation. Unlike neurons, astrocytes only contain soluble endopeptidase 3.4.24.16. Astrocytes secrete the enzyme through monensin, brefeldin A, and forskolin-independent mechanisms. This indicates that endopeptidase 3.4.24.16 is not released by classical regulated or constitutive secreting processes. However, secretion is blocked at 4 degrees C and by 8 bromo cAMP and is enhanced at 42 degrees C, two properties reminiscent of that of other secreted proteins lacking a classical signal peptide. By contrast, neurons appear unable to secrete endopeptidase 3.4.24.16.
Figures





References
-
- Barelli H, Vincent JP, Checler F. Peripheral inactivation of neurotensin: isolation and characterization of a metallopeptidase from rat ileum. Eur J Biochem. 1988;175:481–489. - PubMed
-
- Barelli H, Vincent JP, Checler F. Rat kidney endopeptidase 24.16: purification, physico-chemical characteristics and specificity towards opiates, tachykinins and neurotensin-related peptides. Eur J Biochem. 1993;211:79–90. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
