Involvement of a phorbol ester-insensitive protein kinase C in the alpha2-adrenergic inhibition of voltage-gated calcium current in chick sympathetic neurons
- PMID: 8764648
- PMCID: PMC6579019
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.16-15-04596.1996
Involvement of a phorbol ester-insensitive protein kinase C in the alpha2-adrenergic inhibition of voltage-gated calcium current in chick sympathetic neurons
Abstract
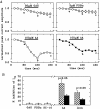
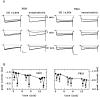
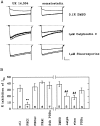
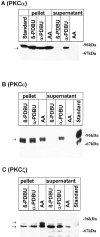
alpha2-Adrenoceptors regulate the efficacy at the sympathoeffector junction by means of a feedback inhibition of transmitter release. In chick sympathetic neurons, the mechanism involves an inhibition of N-type calcium channels, and we now present evidence that this effect involves an atypical, phorbol ester-insensitive protein kinase C (PKC). The inhibition of voltage-gated Ca2+ currents by the specific alpha2-adrenergic agonist UK 14,304 was significantly attenuated when the PKC inhibitors PKC(19-36), staurosporine, or calphostin C were included in the internal solution used to fill the patch pipettes, or if staurosporine or calphostin C were applied extracellularly; however, phorbol esters as classical activators of PKC or oleoylacetylglycerol did not mimic the effect of UK 14,304, and chronic exposure to 4-beta-phorbol dibutyrate (PDBu) did not attenuate it, ever though PKCalpha and -epsilon isozymes were translocated to plasma membranes by PDBu. The atypical isozyme PKCzeta was translocated by 100 micrometer AA and this effect was attenuated when PKC(19-36) was added to the patch pipette solution. Our observations indicate that classical, new, and atypical PKC isozymes are present in chick sympathetic neurons and that an atypical, phorbol ester-insensitive PKC is involved in the inhibition of voltage-activated calcium currents by alpha2-adrenoceptor activation.
Figures
References
-
- Asaoka Y, Nakamura S-I, Yoshida K, Nishizuka Y. Protein kinase C, calcium and phospholipid degradation. Trends Biochem Sci. 1992;17:414–417. - PubMed
-
- Axelrod J. Receptor-mediated activation of phospholipase A2 and arachidonic acid release in signal transduction. Biochem Soc Trans. 1990;18:503–507. - PubMed
-
- Axelrod J, Burch RM, Jelsema CL. Receptor-mediated activation of phospholipase A2 via GTP-binding proteins: arachidonic acid and its metabolites as second messengers. Trends Neurosci. 1988;11:117–123. - PubMed
-
- Beech DJ, Bernheim L, Hille B. Pertussis toxin and voltage dependence distinguish multiple pathways modulating calcium channels of rat sympathetic neurons. Neuron. 1992;8:97–106. - PubMed
-
- Bley KR, Tsien RW. Inhibition of Ca2+ and K+ channels in sympathetic neurons by neuropeptides and other ganglionic transmitters. Neuron. 1990;2:379–391. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
