Selective G-protein regulation of neuronal calcium channels
- PMID: 8764650
- PMCID: PMC6579028
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.16-15-04617.1996
Selective G-protein regulation of neuronal calcium channels
Abstract
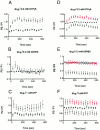
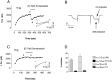
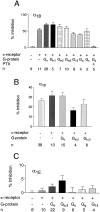
We examined the properties and regulation of Ca channels resulting from the expression of human alpha1B and alpha1E subunits stably expressed in KEK293 cells. The ancillary subunits beta1B and alpha2/delta were also stably expressed in these cell lines. Ca currents in alpha1B-expressing cells had the properties of N-type currents. Ca currents in cells expressing alpha1E exhibited a novel profile that was similar to the properties of the "R type" Ca current. Introduction of GTP-gamma-S into alpha1B cells greatly enhanced the extent of prepulse facilitation of the Ca current, whereas it had only a very small effect in alpha1E-expressing cells. Activation of somatostatin receptors endogenous to HEK293 cells or kappa opioid receptors, expressed in the cells after transfection, inhibited Ca currents in alpha1B-expressing cells. This inhibition was blocked by pertussis toxin and was partially relieved by a depolarizing prepulse. In contrast, no inhibitory effects were noted in cells expressing alpha1E channels under the same circumstances. HEK293 cells normally contained G-proteins from all of the four major families. Inhibition of Ca currents by kappa agonists in alpha1B-expressing cells was enhanced slightly by the cotransfection of several G-protein alpha subunits. kappa agonists, however, had no effect in alpha1E-containing cells, even after overexpression of different G-protein alpha-subunits. In summary, these results demonstrate that there is a large difference in the susceptibility of alpha1B- and alpha1E-based Ca channels to regulation by G-proteins. This is so despite the fact that the two types of Ca channels show substantial similarities in their primary sequences.
Figures



References
-
- Andersson S, Davis DL, Dahlback H, Jornvall H, Russell DW. Cloning, structure and expression of the mitochondrial cytochrome P-450 sterol 25-hydroxylase, a bile acid biosynthetic enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1989;264:8222–8229. - PubMed
-
- Ausubel FM, Brent R, Kingston RE, Moore DD, Seidman JG, Smith JA, Struhl K. Current protocols in molecular biology, Wiley; New York: 1993. Transfection of DNA into eukaryotic cells. pp. 9.1.1–9.1.7.
-
- Avidor-Reiss T, Zippel R, Levy R, Saya D, Ezra V, Barg J, Matus-Leibovitch N, Vogel Z. κ-opioid receptor transfected cell lines: modulation of adenylyl cyclase activity following acute and chronic opioid treatment. FEBS Lett. 1995;361:70–74. - PubMed
-
- Bean BP. Neurotransmitter inhibition of neuronal calcium channels by changes in channel voltage dependence. Nature. 1989;340:153–156. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
