Is the comorbidity of epilepsy and migraine due to a shared genetic susceptibility?
- PMID: 8857719
- PMCID: PMC2791701
- DOI: 10.1212/wnl.47.4.918
Is the comorbidity of epilepsy and migraine due to a shared genetic susceptibility?
Abstract
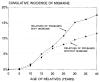
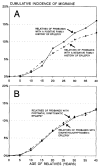
We tested the hypothesis that the comorbidity of migraine and epilepsy results from a shared genetic susceptibility to the two disorders. We used semistructured telephone interviews to collect information on migraine and epilepsy in the families (parents, siblings, and offspring) of 1,967 adult probands with epilepsy. Epilepsy was defined as a lifetime history of two or more unprovoked seizures, and migraine as self-reported severe headaches with two or more of the following symptoms: unilateral pain, throbbing pain, visual aura, or nausea. As a first test of the hypothesis of shared susceptibility, we assessed risk of migraine in relatives of probands with genetic versus nongenetic forms of epilepsy, using two proxy measures of genetic susceptibility-a first-degree family history of epilepsy and idiopathic/cryptogenic (versus postnatal symptomatic) etiology. Neither of these two measures was associated with risk of migraine in relatives. As a second test, we assessed risk of epilepsy in the relatives of probands with versus without migraine. With the exception of one subgroup (sons of female probands), risk of epilepsy in relatives was not associated with the proband's history of migraine. This pattern of results is inconsistent with the hypothesis of a shared genetic susceptibility to migraine and epilepsy.
Figures
References
-
- Stewart WF, Lipton RB, Celentano DD, Reed ML. Prevalence of migraine headache in the United States: relation to age, income, race, and other sociodemographic factors. JAMA. 1992;267:64–69. - PubMed
-
- Hauser WA, Annegers JF, Kurland LT. Prevalence of epilepsy in Rochester, Minnesota: 1940–1980. Epilepsia. 1991;32:429–445. - PubMed
-
- Andermann E, Andermann F. Migraine-epilepsy relationships: epidemiological and genetic aspects. In: Andermann FA, Lugaresi E, editors. Migraine and epilepsy. Butter-worth; Boston: 1987. pp. 281–291.
-
- Ottman R, Lipton RB. Comorbidity of migraine and epilepsy. Neurology. 1994;44:2105–2110. - PubMed
-
- Shechter A, Stewart W, Celentano D, Linet M. An epidemiologic study of migraine and head injury [abstract] Neurology. 1990;40(suppl 1):345.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
