Prognostic factors of patients with thymoma
- PMID: 8882475
- PMCID: PMC4532000
- DOI: 10.3904/kjim.1996.11.1.40
Prognostic factors of patients with thymoma
Abstract
Objectives: To analyze the prognostic factors influencing the survival of patients with thymoma, clinical characteristics, treatment modalities and survival of patients were evaluated. The efficacy of chemotherapy was also determined.
Methods: Retrospective study was done on one hundred patients whose diagnosis was confirmed pathologically at Seoul National University Hospital from 1981 to 1994. The staging was carried out according to the Masaoka system. Survival rate was calculated by the Kaplan-Meier method and prognostic factors were analyzed by a multivariate analysis (Weibull model).
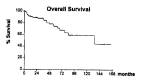
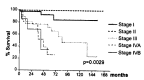
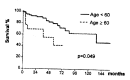
Results: The stage of 100 patients was as follows: Stage I-50, II-6, III-27, IV A-10, IV B-7. The overall survival rates at 5 and 10 years after diagnosis were 73.1% and 58.7%, respectively. The 5-year survival differences, according to various prognostic factors, were as follows: 1) Stage: I-92.8%, II-100%, III-71.6%, IVA-25.9% and IVB-32.9% (p = 0.0029). 2) Age: < 60 years-79.5% and > or = 60 years-41.5% (p = 0.0489). 3) Extent of resection: Total patients: complete resection-87.6% and incomplete resection-50.5% (p > 0.05) Stage III: complete resection-66.7% and incomplete resection-75.5% (p > 0.05) 4) Myasthenia gravis: present-71.6% and absent-74.9% (p > 0.05) Seventeen patients were treated with a combination chemotherapy of Cyclophosphamide, Adriamycin and cisplatin(CAP). Two complete responses and seven partial responses (overall response rate of 53%) were observed with a median response duration of fourteen months. Combination chemotherapy with CAP was effective.
Conclusions: Stage and age were the independent prognostic factors in patients with thymoma. However, the presence of myasthenia gravis or the extent of resection in stage III patients was not associated with the survival time.
Figures

References
-
- Rosenberg JC. Neoplasms of the mediastinum. In: DeVita VT Jr, Hellman S, Rosenberg SA, editors. Cancer: Principles and Practice of Oncology. 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott; 1993. pp. 759–770.
-
- Rosai J, Levine GD. Tumor of the thymomas of the thymus. In: Harlan I, Ferminger MD, editors. Atlas of tumor pathology, series 2, Fascicle 13. Washinton, DC: Armed Forces Institute of Pathology; 1976. pp. 34–161.
-
- Lauriola L, Maggiano N, Marino M, Carbone A, Piantelli M, Musiani P. Human thymoma: Immunologic characteristics of the lymphocyte component. Cancer. 1981;48:1992. - PubMed
-
- Jain U, Frable WJ. Thymoma: Analysis of benign and malignant criteria. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1974;67:310–321. - PubMed
-
- Levine GD, Rosai J. Thymic hyperplasia and neoplasia: A review of current concepts. Hum Pathol. 1978;9:495–515. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
