Pharyngitis
- PMID: 8890141
- PMCID: PMC7125999
- DOI: 10.1016/s0095-4543(05)70359-6
Pharyngitis
Abstract
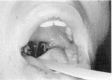
This article reviews the commonly encountered agents causing acute inflammation of the pharynx and tonsils, with special attention to a practical approach for identifying and dealing with the group A beta-hemolytic streptococcus. Ubiquitous viral agents such as Epstein-Barr virus, rhinovirus, and adenovirus are reviewed. Some agents such as group A beta-hemolytic streptococcus and Epstein-Barr virus are susceptible to treatment. Additionally, unusual infectious agents and noninfectious causes of pharyngitis are enumerated.
Figures


References
-
- Baum S.G. Adenovirus. In: Mandell G., Dolin R., Bennett D., editors. Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases. ed 4. Churchill-Livingstone; New York: 1995. p. 1382.
-
- Bertin L., Pons G., d'Athis P. Randomized, double-blind, multicenter, controlled trial of ibuprofen versus acetaminophen (paracetamol) and placebo for treatment of symptoms of tonsillitis and pharyngitis in children. J Pediatr. 1991;119:811. - PubMed
-
- Bisno A.L. Group A streptococcal infections and acute rheumatic fever. N Engl J Med. 1991;35:783. - PubMed
-
- Block S.L., Hedrick J.A., Tyler R.D. Comparative study of the effectiveness of cefixime and penicillin V for the treatment of streptococcal pharyngitis in children and adolescents. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1993;11:919. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

