Heteromultimeric CLC chloride channels with novel properties
- PMID: 8917596
- PMCID: PMC24098
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.93.23.13362
Heteromultimeric CLC chloride channels with novel properties
Abstract
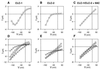
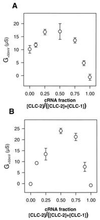
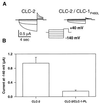
The skeletal muscle chloride channel CLC-1 and the ubiquitous volume-activated chloride channel CLC-2 belong to a large gene family whose members often show overlapping expression patterns. CLC-1 and CLC-2 are coexpressed in skeletal and smooth muscle and in the heart. By coexpressing CLC-1 and CLC-2 in Xenopus oocytes, we now show the formation of novel CLC-1/CLC-2 heterooligomers that yield time-independent linear chloride currents with a chloride-->bromide-->iodide selectivity sequence. Formation of heterooligomeric CLC channels increases the number and possible functions of chloride channels.
Figures

References
-
- Jentsch T J. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 1996;6:303–310. - PubMed
-
- Gründer S, Thiemann A, Pusch M, Jentsch T J. Nature (London) 1992;360:759–762. - PubMed
-
- Steinmeyer K, Klocke R, Ortland C, Gronemeier M, Jockusch H, Gründer S, Jentsch T J. Nature (London) 1991;354:304–308. - PubMed
-
- Uchida S, Sasaki S, Furukawa T, Hiraoka M, Imai T, Hirata Y, Marumo F. J Biol Chem. 1993;268:3821–3824. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

