NMR characterization and solution structure determination of the oxidized cytochrome c7 from Desulfuromonas acetoxidans
- PMID: 8962062
- PMCID: PMC26143
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.93.25.14396
NMR characterization and solution structure determination of the oxidized cytochrome c7 from Desulfuromonas acetoxidans
Abstract
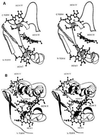
The solution structure of the three-heme electron transfer protein cytochrome c7 from Desulfuromonas acetoxidans is reported. The determination of the structure is obtained through NMR spectroscopy on the fully oxidized, paramagnetic form. The richness of structural motifs and the presence of three prosthetic groups in a protein of 68 residues is discussed in comparison with the four-heme cytochromes c3 already characterized through x-ray crystallography. In particular, the orientation of the three hemes present in cytochrome c7 is similar to that of three out of four hemes of cytochromes c3. The reduction potentials of the individual hemes, which have been obtained through the sequence-specific assignment of the heme resonances, are discussed with respect to the properties of the protein matrix. This information is relevant for any attempt to understand the electron transfer pathway.
Figures

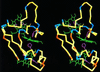
References
-
- Ambler R P. In: From Cyclotrons to Cytochromes. Robinson A B, Kaplan N O, editors. London: Academic; 1980. pp. 263–279.
-
- Pettigrew G W, Moore G R. Cytochromes C: Biological Aspects. Berlin: Springer; 1987.
-
- Haser R, Pierrot M, Frey M, Payan F, Astier J P, Bruschi M, LeGall J. Nature (London) 1979;282:806–810. - PubMed
-
- Pierrot M, Haser R, Frey M, Payan F, Astier J P. J Biol Chem. 1982;257:14341–14348. - PubMed
-
- Higuchi Y, Kusunoki M, Matsuura Y, Yasuoka N, Kakudo M. J Mol Biol. 1984;172:109–139. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

