Mouse cytoplasmic polyadenylylation element binding protein: an evolutionarily conserved protein that interacts with the cytoplasmic polyadenylylation elements of c-mos mRNA
- PMID: 8962099
- PMCID: PMC26180
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.93.25.14602
Mouse cytoplasmic polyadenylylation element binding protein: an evolutionarily conserved protein that interacts with the cytoplasmic polyadenylylation elements of c-mos mRNA
Abstract
Cytoplasmic polyadenylylation is an essential process that controls the translation of maternal mRNAs during early development and depends on two cis elements in the 3' untranslated region: the polyadenylylation hexanucleotide AAUAAA and a U-rich cytoplasmic polyadenylylation element (CPE). In searching for factors that could mediate cytoplasmic polyadenylylation of mouse c-mos mRNA, which encodes a serine/threonine kinase necessary for oocyte maturation, we have isolated the mouse homolog of CPEB, a protein that binds to the CPEs of a number of mRNAs in Xenopus oocytes and is required for their polyadenylylation. Mouse CPEB (mCPEB) is a 62-kDa protein that binds to the CPEs of c-mos mRNA. mCPEB mRNA is present in the ovary, testis, and kidney; within the ovary, this RNA is restricted to oocytes. mCPEB shows 80% overall identity with its Xenopus counterpart, with a higher homology in the carboxyl-terminal portion, which contains two RNA recognition motifs and a cysteine/histidine repeat. Proteins from arthropods and nematodes are also similar to this region, suggesting an ancient and widely used mechanism to control polyadenylylation and translation.
Figures


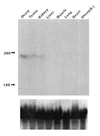


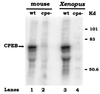

References
-
- Richter J. In: Translational Control. Hershey J W B, Mathews M B, Sonenberg N, editors. Plainview, NY: Cold Spring Harbor Lab. Press; 1996. pp. 481–503.
-
- Vassalli J, Stutz A. Curr Biol. 1995;5:476–479. - PubMed
-
- Sallés F, Lieberfarb M, Wreden C, Gergen J, Strickland S. Science. 1994;266:1996–1998. - PubMed
-
- Simon R, Wu L, Richter J D. Dev Biol. 1996;179:239–250. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

