Length suppression in histone messenger RNA 3'-end maturation: processing defects of insertion mutant premessenger RNAs can be compensated by insertions into the U7 small nuclear RNA
- PMID: 8962110
- PMCID: PMC26191
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.93.25.14659
Length suppression in histone messenger RNA 3'-end maturation: processing defects of insertion mutant premessenger RNAs can be compensated by insertions into the U7 small nuclear RNA
Abstract
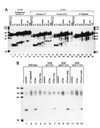
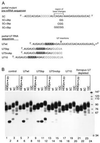
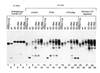
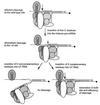
Efficient 3'-end processing of cell cycle-regulated mammalian histone premessenger RNAs (pre-mRNAs) requires an upstream stem-loop and a histone downstream element (HDE) that base pairs with the U7 small ribonucleoprotein. Insertions between these elements have two effects: the site of cleavage moves in concert with the HDE and processing efficiency declines. We used Xenopus oocytes to ask whether compensatory length insertions in the human U7 RNA could restore the fidelity and efficiency of processing of mouse histone insertion pre-mRNAs. An insertion of 5 nt into U7 RNA that extends its complementary to the HDE compensated for both defects in processing of a 5-nt insertion substrate; a noncomplementary insertion into U7 did not. Yet, the noncomplementary insertion mutant U7 was shown to be active on insertion substrates further mutated to allow base pairing. Our results suggest that the histone pre-mRNA becomes rigidified upstream of its HDE, allowing the bound U7 small ribonucleoprotein to measure from the HDE to the cleavage site. Such a mechanism may be common to other RNA measuring systems. To our knowledge, this is the first demonstration of length suppression in an RNA processing system.
Figures

Similar articles
-
3' end processing of mouse histone pre-mRNA: evidence for additional base-pairing between U7 snRNA and pre-mRNA.Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Oct 11;22(20):4023-30. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.20.4023. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994. PMID: 7937126 Free PMC article.
-
A synthetic histone pre-mRNA-U7 small nuclear RNA chimera undergoing cis cleavage in the cytoplasm of Xenopus oocytes.Nucleic Acids Res. 1995 Aug 25;23(16):3152-60. doi: 10.1093/nar/23.16.3152. Nucleic Acids Res. 1995. PMID: 7667091 Free PMC article.
-
The site of 3' end formation of histone messenger RNA is a fixed distance from the downstream element recognized by the U7 snRNP.EMBO J. 1994 May 15;13(10):2432-40. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06528.x. EMBO J. 1994. PMID: 8194533 Free PMC article.
-
U7 deciphered: the mechanism that forms the unusual 3' end of metazoan replication-dependent histone mRNAs.Biochem Soc Trans. 2021 Nov 1;49(5):2229-2240. doi: 10.1042/BST20210323. Biochem Soc Trans. 2021. PMID: 34351387 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Formation of the 3' end of histone mRNA.Gene. 1999 Oct 18;239(1):1-14. doi: 10.1016/s0378-1119(99)00367-4. Gene. 1999. PMID: 10571029 Review.
Cited by
-
Cotranscriptional processing of Drosophila histone mRNAs.Mol Cell Biol. 2003 Jun;23(12):4046-55. doi: 10.1128/MCB.23.12.4046-4055.2003. Mol Cell Biol. 2003. PMID: 12773550 Free PMC article.
-
Evolutionary patterns of non-coding RNAs.Theory Biosci. 2005 Apr;123(4):301-69. doi: 10.1016/j.thbio.2005.01.002. Theory Biosci. 2005. PMID: 18202870
-
Dual role for the RNA-binding domain of Xenopus laevis SLBP1 in histone pre-mRNA processing.RNA. 2000 Nov;6(11):1635-48. doi: 10.1017/s1355838200000819. RNA. 2000. PMID: 11105762 Free PMC article.
-
Binding of human SLBP on the 3'-UTR of histone precursor H4-12 mRNA induces structural rearrangements that enable U7 snRNA anchoring.Nucleic Acids Res. 2006;34(17):4987-95. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkl666. Epub 2006 Sep 18. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006. PMID: 16982637 Free PMC article.
-
Studies of the 5' exonuclease and endonuclease activities of CPSF-73 in histone pre-mRNA processing.Mol Cell Biol. 2009 Jan;29(1):31-42. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00776-08. Epub 2008 Oct 27. Mol Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 18955505 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

