Cross-linking of Fas by antibodies to a peculiar domain of gp120 V3 loop can enhance T cell apoptosis in HIV-1-infected patients
- PMID: 8976184
- PMCID: PMC2196362
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.184.6.2287
Cross-linking of Fas by antibodies to a peculiar domain of gp120 V3 loop can enhance T cell apoptosis in HIV-1-infected patients
Abstract
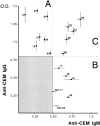
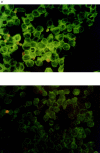
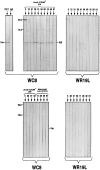
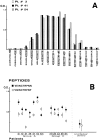
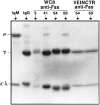
Previous studies have demonstrated that T cell-reactive antibodies in HIV-1 infection contribute to lymphocyte depletion by cytotoxicity that involves differential membrane targets, such as the 43.5-kD receptor on CEM cells. Here, we show that these antibodies bind Fas as result of a molecular mimicry of the gp120. Both flow cytometry and immunoblotting using the human Fas-transfected mouse WC8 lymphoma revealed positive binding of immunoglobulin G from several patients to a 43.8-kD membrane receptor that also reacts with the CH11 anti-Fas monoclonal antibody. Specificity to Fas was further confirmed to chimeric recombinant human Fas-Fc by ELISA, whereas overlapping peptide mapping of a Fas domain (VEINCTR-N) shared by gp120 V3 loop demonstrated a predominant affinity to the full-length 10-mer peptide. Four anti-Fas affinity preparations greatly increased the subdiploid DNA peak of CEM cells similar to agonist ligands of Fas. In addition, anti-Fas immunoglobulin G strongly inhibited the [3H]thymidine uptake of CEM cells in proliferative assays, inducing a suppression as high as provoked by both CH11 mAb and recombinant human Fas ligand. Since anti-Fas were reactive to gp120, it is conceivable that antibodies binding that domain within the V3 region are effective cross-linkers of Fas and increase apoptosis in peripheral T cells. These results suggest that autologous stimulation of the Fas pathway, rather than of lymphocytotoxic antibodies, may aggravate lymphopenia in a number of HIV-1+ subjects.
Figures



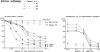
Similar articles
-
Immunogenicity of an eight amino acid domain shared by Fas (CD95/Apo-I) and HIV-1 gp120. I. Structural and antigenic analysis.Mol Med. 2000 Jun;6(6):494-508. Mol Med. 2000. PMID: 10972086 Free PMC article.
-
VEINCTR-N, an immunogenic epitope of Fas (CD95/Apo-I), and soluble Fas enhance T-cell apoptosis in vitro. II. Functional analysis and possible implications in HIV-1 disease.Mol Med. 2000 Jun;6(6):509-26. Mol Med. 2000. PMID: 10972087 Free PMC article.
-
Design of immunogens that present the crown of the HIV-1 V3 loop in a conformation competent to generate 447-52D-like antibodies.Biochem J. 2006 Nov 1;399(3):483-91. doi: 10.1042/BJ20060588. Biochem J. 2006. PMID: 16827663 Free PMC article.
-
HIV-1 induced AIDS is an allergy and the allergen is the Shed gp120--a review, hypothesis, and implications.Virus Genes. 2004 Apr;28(3):319-31. doi: 10.1023/b:viru.0000025778.56507.61. Virus Genes. 2004. PMID: 15266113 Review.
-
AIDS and the death receptors.Br Med Bull. 1997;53(3):604-16. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a011633. Br Med Bull. 1997. PMID: 9374040 Review.
Cited by
-
Fas/Fas ligand (FasL)-deregulated apoptosis and IL-6 insensitivity in highly malignant myeloma cells.Clin Exp Immunol. 1998 Nov;114(2):179-88. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.1998.00711.x. Clin Exp Immunol. 1998. PMID: 9822274 Free PMC article.
-
HIV-1 kills renal tubular epithelial cells in vitro by triggering an apoptotic pathway involving caspase activation and Fas upregulation.J Clin Invest. 1998 Dec 15;102(12):2041-9. doi: 10.1172/JCI3480. J Clin Invest. 1998. PMID: 9854039 Free PMC article.
-
Cytopathic killing of peripheral blood CD4(+) T lymphocytes by human immunodeficiency virus type 1 appears necrotic rather than apoptotic and does not require env.J Virol. 2002 May;76(10):5082-93. doi: 10.1128/jvi.76.10.5082-5093.2002. J Virol. 2002. PMID: 11967324 Free PMC article.
-
Human immunodeficiency virus-1 (HIV-1)-mediated apoptosis: new therapeutic targets.Viruses. 2014 Aug 19;6(8):3181-227. doi: 10.3390/v6083181. Viruses. 2014. PMID: 25196285 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Laurent-Crawford AG, Krust B, Muller S, Riviere Y, Rey-Cuillè MA, Bechet JM, Montagnier L, Hovanessian AG. The cytopathic effect of HIV is associated with apoptosis. Virology. 1991;185:829–838. - PubMed
-
- Meyaard L, Otto SA, Jonker RR, Mijnster MJ, Keet RP, Miedema F. Programmed death of T cells in HIV-1 infection. Science (Wash DC) 1992;257:217–219. - PubMed
-
- Gougeon ML, Laurent-Crawford AG, Hovanessian AG, Montagnier L. Direct and indirect mechanism mediating apoptosis during HIV infection: contribution to in vivo CD4 T cell depletion. Semin Immunol. 1993;5:187–196. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

