Changes in hippocampal circuitry after pilocarpine-induced seizures as revealed by opioid receptor distribution and activation
- PMID: 8987772
- PMCID: PMC6793675
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.17-01-00477.1997
Changes in hippocampal circuitry after pilocarpine-induced seizures as revealed by opioid receptor distribution and activation
Abstract
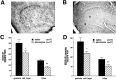
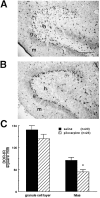
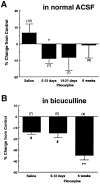
The pilocarpine model of temporal lobe epilepsy was used to study the time-dependent changes in dentate gyrus circuitry after seizures. Seizures caused a decrease in mu- and delta-opioid receptor immunoreactive (MOR-IR and DOR-IR, respectively) neurons in the hilus and MOR-IR neurons in the granule cell layer. Additionally, diffuse DOR-IR, MOR-IR, and GABA immunoreactivities (GABA-IR) were increased in the inner molecular layer. Using the in vitro hippocampal slice preparation to study the physiological consequences of the anatomical changes, we found that the disinhibitory effects of the mu-opioid receptor agonist [D-Ala2, MePhe4,Gly-(ol)5]-enkephalin (DAMGO) and the GABAA receptor antagonist bicuculline were greatly depressed 5-13 d after pilocarpine injection but returned to control levels within 6 weeks. The amplitudes of monosynaptic evoked IPSCs and the effects of DAMGO on this parameter were also slightly decreased 5-13 d after pilocarpine injection but significantly increased at 6 weeks. DAMGO significantly decreased the mean amplitude of spontaneous IPSCs (sIPSCs) at 6 weeks after pilocarpine injection but not in controls. The delta-opioid receptor agonist [D-Pen2,5]-enkephalin (DPDPE) principally inhibited excitatory transmission in saline-treated animals without affecting either sIPSCs or evoked IPSCs. The DPDPE-induced inhibition of excitatory transmission became more pronounced at 6 weeks after pilocarpine injection. These results illustrate the anatomical reorganization and functional changes in dentate gyrus circuitry evident in an animal model of temporal lobe epilepsy and provide evidence of compensatory changes after trauma to the hippocampal formation.
Figures






References
-
- Adams JC. Biotin amplification of biotin and horseradish peroxidase signals in histochemical stains. J Histochem Cytochem. 1992;40:1457–1463. - PubMed
-
- Alreja M, Aghajanian GK. QX-314 blocks the potassium but not the sodium-dependent component of the opiate response in locus coeruleus neurons. Brain Res. 1994;639:320–324. - PubMed
-
- Amaral DG. A golgi study of cell types in the hilar region of the hippocampus in the rat. J Comp Neurol. 1978;182:851–914. - PubMed
-
- Andrade R. Blockade of neurotransmitter-activated K+ conductance by QX-314 in the rat hippocampus. Eur J Pharmacol. 1991;199:259–262. - PubMed
-
- Baez LA, Eskridge NK, Schein R. Postnatal development of dopaminergic and cholinergic catalepsy in the rat. Eur J Pharmacol. 1976;36:155–162. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
