Resetting the biological clock: mediation of nocturnal CREB phosphorylation via light, glutamate, and nitric oxide
- PMID: 8987789
- PMCID: PMC6573241
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.17-02-00667.1997
Resetting the biological clock: mediation of nocturnal CREB phosphorylation via light, glutamate, and nitric oxide
Abstract
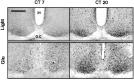
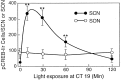
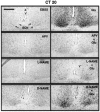
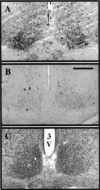
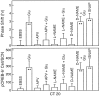
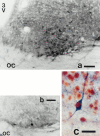
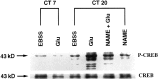
Synchronization between the environmental lighting cycle and the biological clock in the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN) is correlated with phosphorylation of the Ca2+/cAMP response element binding protein (CREB) at the transcriptional activating site Ser133. Mechanisms mediating the formation of phospho-CREB (P-CREB) and their relation to clock resetting are unknown. To address these issues, we probed the signaling pathway between light and P-CREB. Nocturnal light rapidly and transiently induced P-CREB-like immunoreactivity (P-CREB-lir) in the rat SCN. Glutamate (Glu) or nitric oxide (NO) donor administration in vitro also induced P-CREB-lir in SCN neurons only during subjective night. Clock-controlled sensitivity to phase resetting by light. Glu, and NO is similarly restricted to subjective night. The effects of NMDA and nitric oxide synthase (NOS) antagonists on Glu-mediated induction of P-CREB-lir paralleled their inhibition of phase shifting. Significantly, among neurons in which P-CREB-lir was induced by light were NADPH-diaphorase-positive neurons of the SCN's retinorecipient area. Glu treatment increased the intensity of a 43 kDa band recognized by anti-P-CREB antibodies in subjective night but not day, whereas anti-alpha CREB-lir of this band remained constant between night and day. Inhibition of NOS during Glu stimulation diminished the anti-P-CREB-lir of this 43 kDa band. Together, these data couple nocturnal light, Glu, NMDA receptor activation and NO signaling to CREB phosphorylation in the transduction of brief environmental light stimulation of the retina into molecular changes in the SCN resulting in phase resetting of the biological clock.
Figures

References
-
- Alberini CM, Ghiradi M, Metz R, Kandel ER. C/EBP is an immediate-early gene required for the consolidation of long-term facilitation. Cell. 1994;76:1099–1114. - PubMed
-
- Amir S, Robinson B, Edelstein K. Distribution of NADPH-diaphorase staining and light-induced Fos expression in the rat suprachiasmatic nucleus region supports a role for nitric oxide in the circadian system. Neuroscience. 1995;69:545–555. - PubMed
-
- Bading H, Ginty DD, Greenberg ME. Regulation of gene expression in hippocampal neurons by a distinct calcium signaling pathway. Science. 1993;260:181–186. - PubMed
-
- Bourtchuladze R, Frenguelli B, Blendy J, Cioffi D, Schutz G, Silva AJ. Deficient long-term memory in mice with a targeted mutation of the cAMP-responsive element-binding protein. Cell. 1994;79:59–68. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
