Human alpha4beta2 neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor in HEK 293 cells: A patch-clamp study
- PMID: 8987816
- PMCID: PMC6579202
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.16-24-07880.1996
Human alpha4beta2 neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor in HEK 293 cells: A patch-clamp study
Abstract
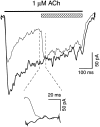
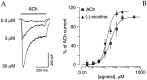
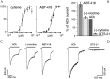
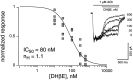
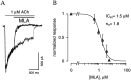
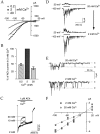
The cloning and expression of genes encoding for the human neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs) has opened new possibilities for investigating their physiological and pharmacological properties. Cells (HEK 293) stably transfected with two of the major brain subunits, alpha4 and beta2, were characterized electrophysiologically using the patch-clamp technique. Fast application of the natural ligand ACh can evoke currents up to 3500 pA, with an apparent affinity (EC50) of 3 microM and a Hill coefficient of 1.2. The rank order of potency of four nAChR ligands to activate human alpha4beta2 receptors is (-)-nicotine > ACh > (-)-cytisine > ABT-418. At saturating concentrations, the efficacy of these ligands is ABT-418 >> (-)-nicotine > ACh >> (-)-cytisine > GTS-21 (previously named DMXB). Coapplication of 1 microM ACh with known nAChR inhibitors such as dihydro-beta-erythroidine and methyllycaconitine reversibly reduces the current evoked by the agonist with respective IC50 values of 80 nM and 1.5 microM. The current-voltage relationship of human alpha4beta2 displays a strong rectification at positive potentials. Experiments of ionic substitutions suggest that human alpha4beta2 nAChRs are permeable to sodium and potassium ions. In the "outside-out" configuration, ACh evokes unitary currents (main conductance 46 pS) characterized by a very fast rundown. Potentiation of the ACh-evoked currents is observed when the extracellular calcium concentration is increased from 0.2 to 2 mM. In contrast, however, a reduction of the evoked currents is observed when calcium concentration is elevated above 2 mM.
Figures
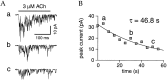
References
-
- Albuquerque EX, Pereira EF, Castro NG, Alkondon M, Reinhardt S, Schroder H, Maelicke A. Nicotinic receptor function in the mammalian central nervous system. Ann NY Acad Sci. 1995;757:48–72. - PubMed
-
- Alkondon M, Albuquerque EX. Diversity of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in rat hippocampal neurons. I. Pharmacological and functional evidence for distinct structural subtypes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1993;265:1455–1473. - PubMed
-
- Arendash GW, Sengstock GJ, Sandberg PR, Kem WR. Improved learning and memory in aged rats with chronic administration of the nicotinic receptor agonist GTS-21. Brain Res. 1995;674:252–259. - PubMed
-
- Arneric SP, Sullivan JP, Briggs CA, Donnelly RD, Anderson DJ, Raszkiewicz JL, Hughes ML, Cadman ED, Adams P, Garvey DS, Wasicak JT, Williams M. (S)-3-methyl-5-(1-methyl-2-pyrrolidinyl) isoxazole (ABT-418): a novel cholinergic ligand with cognition-enhancing and anxiolytic activities: I. In vitro characterization. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1994;270:310–318. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
