Effects of chronic treatment with delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol on cannabinoid-stimulated [35S]GTPgammaS autoradiography in rat brain
- PMID: 8987831
- PMCID: PMC6579228
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.16-24-08057.1996
Effects of chronic treatment with delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol on cannabinoid-stimulated [35S]GTPgammaS autoradiography in rat brain
Abstract
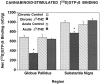
Chronic Delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol (Delta9-THC) administration produces tolerance to cannabinoid effects, but alterations in signal transduction that mediate these changes are not yet known. The present study uses in vitro autoradiography of agonist-stimulated [35S]GTPgammaS binding to localize cannabinoid receptor-activated G-proteins after chronic Delta9-THC treatment. Cannabinoid (WIN 55212-2)-stimulated [35S]GTPgammaS binding was performed in brain sections from rats treated chronically with 10 mg/kg Delta9-THC for 21 d. Control animals received saline or an acute injection of Delta9-THC. Acute Delta9-THC treatment had no effect on basal or WIN 55212-2-stimulated [35S]GTPgammaS binding. After chronic Delta9-THC treatment, net WIN 55212-2-stimulated [35S]GTPgammaS binding was reduced significantly (up to 70%) in most brain regions, including the hippocampus, caudate-putamen, perirhinal and entorhinal cortex, globus pallidus, substantia nigra, and cerebellum. In contrast, chronic Delta9-THC treatment had no effect on GABAB-stimulated [35S]GTPgammaS binding. In membranes and brain sections, Delta9-THC was a partial agonist, stimulating [35S]GTPgammaS by only 20% of the level stimulated by WIN 55212-2 and inhibiting WIN 55212-2-stimulated [35S]GTPgammaS at high concentrations. Because the EC50 of WIN 55212-2-stimulated [35S]GTPgammaS binding and the KD of cannabinoid receptor binding were unchanged by chronic Delta9-THC treatment, the partial agonist actions of Delta9-THC did not produce the decrease in cannabinoid-stimulated [35S]GTPgammaS binding. These results suggest that profound desensitization of cannabinoid-activated signal transduction mechanisms occurs after chronic Delta9-THC treatment.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Cannabinoid receptor and WIN-55,212-2-stimulated [35S]GTP gamma S binding and cannabinoid receptor mRNA levels in the basal ganglia and the cerebellum of adult male rats chronically exposed to delta 9-tetrahydrocannabinol.J Mol Neurosci. 1998 Oct;11(2):109-19. doi: 10.1385/JMN:11:2:109. J Mol Neurosci. 1998. PMID: 10096037
-
Chronic delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol treatment produces a time-dependent loss of cannabinoid receptors and cannabinoid receptor-activated G proteins in rat brain.J Neurochem. 1999 Dec;73(6):2447-59. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.1999.0732447.x. J Neurochem. 1999. PMID: 10582605
-
Cannabinoid receptor and WIN-55,212-2-stimulated [35S]GTPgammaS binding and cannabinoid receptor mRNA levels in several brain structures of adult male rats chronically exposed to R-methanandamide.Neurochem Int. 1999 Jun;34(6):473-82. doi: 10.1016/s0197-0186(99)00020-0. Neurochem Int. 1999. PMID: 10402222
-
Cannabinoid pharmacology: implications for additional cannabinoid receptor subtypes.Chem Phys Lipids. 2002 Dec 31;121(1-2):57-63. doi: 10.1016/s0009-3084(02)00146-9. Chem Phys Lipids. 2002. PMID: 12505690 Review.
-
An overview on functional receptor autoradiography using [35S]GTPgammaS.Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 2001 Dec;38(1-2):149-64. doi: 10.1016/s0165-0173(01)00106-0. Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 2001. PMID: 11750931 Review.
Cited by
-
Sex Differences in Tolerance to Delta-9-Tetrahydrocannabinol in Mice With Cisplatin-Evoked Chronic Neuropathic Pain.Front Mol Biosci. 2021 Jun 25;8:684115. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.684115. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Biosci. 2021. PMID: 34250019 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of cannabinoids on glutamate levels in the human brain: a systematic review and meta-analysis.J Cannabis Res. 2025 Apr 21;7(1):21. doi: 10.1186/s42238-025-00277-9. J Cannabis Res. 2025. PMID: 40259403 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The endocannabinoid system as a target for the treatment of cannabis dependence.Neuropharmacology. 2009;56 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):235-43. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2008.07.018. Epub 2008 Jul 19. Neuropharmacology. 2009. PMID: 18691603 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long-term behavioral and pharmacodynamic effects of delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol in female rats depend on ovarian hormone status.Addict Biol. 2011 Jan;16(1):64-81. doi: 10.1111/j.1369-1600.2010.00227.x. Addict Biol. 2011. PMID: 21158010 Free PMC article.
-
Endocannabinoid tone versus constitutive activity of cannabinoid receptors.Br J Pharmacol. 2011 Aug;163(7):1329-43. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01364.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21545414 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abood ME, Sauss C, Fan F, Tilton CL, Martin BR. Development of behavioral tolerance to Δ9-THC without alteration of cannabinoid receptor binding or mRNA levels in whole brain. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1993;46:575–579. - PubMed
-
- Aceto MD, Scates SM, Lowe JA, Martin BR. Cannabinoid precipitated withdrawal by the selective cannabinoid receptor antagonist, SR 141716A. Eur J Pharmacol. 1995;282:R1–R2. - PubMed
-
- Carlini EA. Tolerance to chronic administration of cannabis sativa (marijuana) in rats. Pharmacology. 1968;1:135–142. - PubMed
-
- Compton DR, Rice KC, DeCosta BR, Razdan RK, Melvin LS, Johnson MR, Martin BR. Cannabinoid structure-activity relationships: correlation of receptor binding and in vivo activities. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1993;265:218–226. - PubMed
-
- De Fonseca FR, Gorriti MA, Fernandez-Ruiz JJ, Palomo T, Ramos JA. Downregulation of rat brain cannabinoid binding sites after chronic Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol treatment. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1994;47:33–40. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
