The choroid plexus epithelium is the site of the organic anion transport protein in the brain
- PMID: 8990200
- PMCID: PMC19316
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.94.1.283
The choroid plexus epithelium is the site of the organic anion transport protein in the brain
Abstract
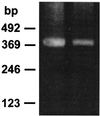
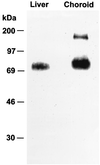
The mRNA for organic anion transport protein (oatp) was previously shown to be present in abundance in liver and kidney, and in small amounts in brain. Data obtained from experiments with reverse transcriptase-PCR techniques and in situ hybridization analysis showed that the oatp mRNA is present within the brain, localized to the choroid plexus. A sequence-specific antibody to the oatp polypeptide demonstrated the presence of the expected polypeptide with a molecular weight of 80,000 plus an immunoreactive species with a higher molecular weight in preparations of choroid plexus membranes. Examination of the choroid plexus by fluorescence confocal microscopy revealed that immunoreactive oatp polypeptide is localized to the apical surface of the choroid plexus epithelial cells, which contacts the cerebrospinal fluid. This localization of oatp is consistent with previous experiments showing vectorial transport of organic anions between the choroid plexus and the cerebrospinal fluid.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

