Abnormal phosphorylation of tau and the mechanism of Alzheimer neurofibrillary degeneration: sequestration of microtubule-associated proteins 1 and 2 and the disassembly of microtubules by the abnormal tau
- PMID: 8990203
- PMCID: PMC19321
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.94.1.298
Abnormal phosphorylation of tau and the mechanism of Alzheimer neurofibrillary degeneration: sequestration of microtubule-associated proteins 1 and 2 and the disassembly of microtubules by the abnormal tau
Abstract
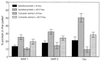
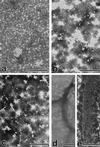
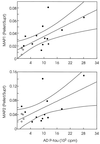
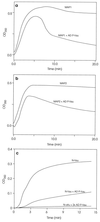
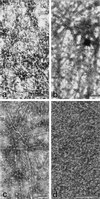
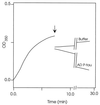
The microtubule-associated protein (MAP) tau is abnormally hyperphosphorylated in Alzheimer disease and accumulates in neurons undergoing neurofibrillary degeneration. In the present study, the associations of the Alzheimer-hyperphosphorylated tau (AD P-tau) with the high molecular weight MAPs (HMW-MAPs) MAP1 and MAP2 were investigated. The AD P-tau was found to aggregate with MAP1 and MAP2 in solution. The association of AD P-tau to the MAPs resulted in inhibition of MAP-promoted microtubule assembly. However, unlike the coaggregation of AD P-tau and normal tau, the association between AD P-tau and the HMW-MAPs did not result in the formation of filaments/tangles. The affinity of the tau-AD P-tau association was higher than that of HMW-MAPs-AD P-tau because normal tau inhibited the latter binding. The association between AD P-tau and the HMW-MAPs also appeared to occur in situ because these proteins cosedimented from the Alzheimer brain extracts, and, in the sediment, the levels of the HMW-MAPs correlated with the levels of AD P-tau. These studies suggested that the abnormally phosphorylated tau can sequester both normal tau and HMW-MAPs and disassemble microtubules but, under physiological conditions, can form tangles of filaments only from tau.
Figures
References
-
- Iqbal, K., Grundke-Iqbal, I., Zaidi, T., Merz, P. A., Wen, G. Y., Shaikh, S. S., Wisniewski, H. M., Alafuzoff, I. & Wimblad, B. (1986) Lancet ii, 421–426. - PubMed
-
- Grundke-Iqbal I, Iqbal K, Quinlan M, Tung Y-C, Zaidi M S, Wisniewski H M. J Biol Chem. 1986;261:6084–6089. - PubMed
-
- Köpke E, Tung Y-C, Shaikh S, Alonso A del C, Iqbal K, Grundke-Iqbal I. J Biol Chem. 1993;268:24374–24384. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

