GABAB receptor-mediated inhibition of tetrodotoxin-resistant GABA release in rodent hippocampal CA1 pyramidal cells
- PMID: 8994057
- PMCID: PMC6573172
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.17-03-01025.1997
GABAB receptor-mediated inhibition of tetrodotoxin-resistant GABA release in rodent hippocampal CA1 pyramidal cells
Abstract
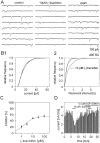
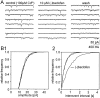
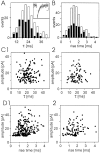
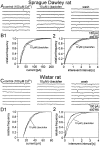
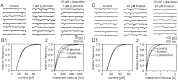
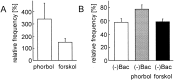
Tight-seal whole-cell recordings from CA1 pyramidal cells of rodent hippocampus were performed to study GABAB receptor-mediated inhibition of tetrodotoxin (TTX)-resistant IP-SCs. IPSCs were recorded in the presence of TTX and glutamate receptor antagonists. (R)-(-)-baclofen reduced the frequency of TTX-resistant IPSCs by a presynaptic action. The inhibition by (R)-(-)-baclofen was concentration-dependent, was not mimicked by the less effective enantiomer (S)-(+)-baclofen, and was blocked by the GABAB receptor antagonist CGP 55845A, suggesting a specific effect on GABAB receptors. The inhibition persisted in the presence of the Ca2+ channel blocker Cd2+. There was no requirement for an activation of K+ conductances by (R)-(-)-baclofen, because the inhibition of TTX-resistant IPSCs persisted in Ba2+ and Cd2+. Because the time courses of TTX-resistant IPSCs were not changed by (R)-(-)-baclofen, there was no evidence for a selective inhibition of quantal release from a subgroup of GABAergic terminals. (R)-(-)-baclofen reduced the frequency of TTX-resistant IPSCs in guinea pigs and Wistar rats, whereas the inhibition was much smaller in Sprague Dawley rats. In Cd2+ and Ba2+, beta-phorbol-12,13-dibutyrate and forskolin enhanced the frequency of TTX-resistant IPSCs. Only beta-phorbol-12, 13-dibutyrate reduced the inhibition by (R)-(-)-baclofen. We conclude that GABAB receptors inhibit TTX-resistant GABA release through a mechanism independent from the well known effects on Ca2+ or K+ channels. The inhibition of quantal GABA release can be reduced by an activator of protein kinase C.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Calcium channel involvement in GABAB receptor-mediated inhibition of GABA release in area CA1 of the rat hippocampus.J Neurophysiol. 1995 Jul;74(1):43-53. doi: 10.1152/jn.1995.74.1.43. J Neurophysiol. 1995. PMID: 7472344
-
Multiple postsynaptic actions of GABA via GABAB receptors on CA1 pyramidal cells of rat hippocampal slices.J Neurophysiol. 1996 Jul;76(1):69-80. doi: 10.1152/jn.1996.76.1.69. J Neurophysiol. 1996. PMID: 8836210
-
GABAB receptor-mediated inhibition of spontaneous inhibitory synaptic currents in rat midbrain culture.J Physiol. 1997 May 1;500 ( Pt 3)(Pt 3):739-49. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1997.sp022055. J Physiol. 1997. PMID: 9161988 Free PMC article.
-
Classics in Chemical Neuroscience: Baclofen.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2020 Jun 17;11(12):1740-1755. doi: 10.1021/acschemneuro.0c00254. Epub 2020 Jun 3. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32436697 Review.
-
Binding of clozapine to the GABAB receptor: clinical and structural insights.Mol Psychiatry. 2020 Sep;25(9):1910-1919. doi: 10.1038/s41380-020-0709-5. Epub 2020 Mar 13. Mol Psychiatry. 2020. PMID: 32203158 Review.
Cited by
-
The GABAB1a isoform mediates heterosynaptic depression at hippocampal mossy fiber synapses.J Neurosci. 2009 Feb 4;29(5):1414-23. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3697-08.2009. J Neurosci. 2009. PMID: 19193888 Free PMC article.
-
Insulin-like growth factor 1 and a cytosolic tyrosine kinase activate chloride outward transport during maturation of hippocampal neurons.J Neurosci. 2001 Nov 1;21(21):8339-47. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-21-08339.2001. J Neurosci. 2001. PMID: 11606621 Free PMC article.
-
GABAA receptor-mediated IPSCs in rat thalamic sensory nuclei: patterns of discharge and tonic modulation by GABAB autoreceptors.J Physiol. 1997 Jul 1;502 ( Pt 1)(Pt 1):91-104. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.1997.091bl.x. J Physiol. 1997. PMID: 9234199 Free PMC article.
-
Neurexins regulate presynaptic GABAB-receptors at central synapses.Nat Commun. 2021 Apr 22;12(1):2380. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-22753-5. Nat Commun. 2021. PMID: 33888718 Free PMC article.
-
NMDA receptor-dependent GABAB receptor internalization via CaMKII phosphorylation of serine 867 in GABAB1.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Aug 3;107(31):13924-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1000909107. Epub 2010 Jul 19. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. PMID: 20643921 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bijak M, Misgeld U. Adrenergic modulation of hilar neuron activity and granule cell inhibition in the guinea-pig hippocampal slice. Neuroscience. 1995;67:541–550. - PubMed
-
- Cohen GA, Doze VA, Madison DV. Opioid inhibition of GABA release from presynaptic terminals of rat hippocampal interneurons. Neuron. 1992;9:325–335. - PubMed
-
- Diversé-Pierluissi M, Dunlap K. Distinct, convergent second messenger pathways modulate neuronal calcium currents. Neuron. 1993;10:753–760. - PubMed
-
- Dolphin AC. Voltage dependent calcium channels and their modulation by neurotransmitters and G proteins. Exp Physiol. 1995;80:1–36. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
