Linkage of a neurophysiological deficit in schizophrenia to a chromosome 15 locus
- PMID: 9012828
- PMCID: PMC19557
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.94.2.587
Linkage of a neurophysiological deficit in schizophrenia to a chromosome 15 locus
Abstract
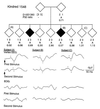
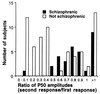
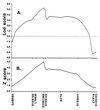
Inheritance of a defect in a neuronal mechanism that regulates response to auditory stimuli was studied in nine families with multiple cases of schizophrenia. The defect, a decrease in the normal inhibition of the P50 auditory-evoked response to the second of paired stimuli, is associated with attentional disturbances in schizophrenia. Decreased P50 inhibition occurs not only in most schizophrenics, but also in many of their nonschizophrenic relatives, in a distribution consistent with inherited vulnerability for the illness. Neurobiological investigations in both humans and animal models indicated that decreased function of the alpha 7-nicotinic cholinergic receptor could underlie the physiological defect. In the present study, a genome-wide linkage analysis, assuming autosomal dominant transmission, showed that the defect is linked [maximum logarithm of the odds (lod) score = 5.3 with zero recombination] to a dinucleotide polymorphism at chromosome 15q13-14, the site of the alpha 7-nicotinic receptor. Despite many schizophrenics' extremely heavy nicotine use, nicotinic receptors were not previously thought to be involved in schizophrenia. The linkage data thus provide unique new evidence that the alpha 7-nicotinic receptor gene may be responsible for the inheritance of a pathophysiological aspect of the illness.
Figures
References
-
- Risch N. Genet Epidemiol. 1990;7:3–16. - PubMed
-
- Tsuang M T. Br J Psychiatry. 1993;163:299–307. - PubMed
-
- Pulver A E, Karayiorgou M, Lasseter V K, Wolyniec P, Kasch L, Antonarakis S, Housman D, Kazazian H H, Meyers D, Nestadt G. Am J Med Genet. 1994;54:44–50. - PubMed
-
- Coon H, Sobell J, Heston L, Sommer S, Hoff M, Holik J, Umar F, Robertson M, Reimherr F, Wender P, Byerley W. Am J Med Genet. 1994;54:12–20. - PubMed
-
- Wang S, Sun C E, Walczak C A, Ziegle J S, Kipps B R, Goldion L R, Diehl S R. Nat Genet. 1995;10:41–46. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

