Structure, subunit topology, and actin-binding activity of the Arp2/3 complex from Acanthamoeba
- PMID: 9015304
- PMCID: PMC2134809
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.136.2.331
Structure, subunit topology, and actin-binding activity of the Arp2/3 complex from Acanthamoeba
Abstract
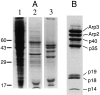
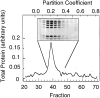
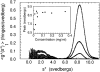
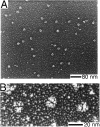
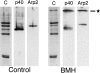
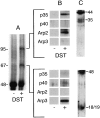
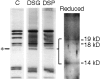
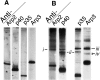
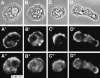
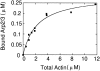
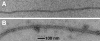
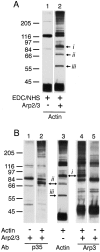
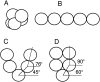
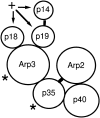
The Arp2/3 complex, first isolated from Acanthamoeba castellani by affinity chromatography on profilin, consists of seven polypeptides; two actin-related proteins, Arp2 and Arp3; and five apparently novel proteins, p40, p35, p19, p18, and p14 (Machesky et al., 1994). The complex is homogeneous by hydrodynamic criteria with a Stokes' radius of 5.3 nm by gel filtration, sedimentation coefficient of 8.7 S, and molecular mass of 197 kD by analytical ultracentrifugation. The stoichiometry of the subunits is 1:1:1:1:1:1:1, indicating the purified complex contains one copy each of seven polypeptides. In electron micrographs, the complex has a bilobed or horseshoe shape with outer dimensions of approximately 13 x 10 nm, and mathematical models of such a shape and size are consistent with the measured hydrodynamic properties. Chemical cross-linking with a battery of cross-linkers of different spacer arm lengths and chemical reactivities identify the following nearest neighbors within the complex: Arp2 and p40; Arp2 and p35; Arp3 and p35; Arp3 and either p18 or p19; and p19 and p14. By fluorescent antibody staining with anti-p40 and -p35, the complex is concentrated in the cortex of the ameba, especially in linear structures, possibly actin filament bundles, that lie perpendicular to the leading edge. Purified Arp2/3 complex binds actin filaments with a Kd of 2.3 microM and a stoichiometry of approximately one complex molecule per actin monomer. In electron micrographs of negatively stained samples, Arp2/3 complex decorates the sides of actin filaments. EDC/NHS cross-links actin to Arp3, p35, and a low molecular weight subunit, p19, p18, or p14. We propose structural and topological models for the Arp2/3 complex and suggest that affinity for actin filaments accounts for the localization of complex subunits to actin-rich regions of Acanthamoeba.
Figures


References
-
- Ackers GK. A new calibration procedure for gel filtration columns. J Biol Chem. 1967;242:3237–3238.
-
- Aebi U, Pollard TD. A glow discharge unit to render electron microscope grids and other surfaces hydrophilic. J Electron Micro Tech. 1987;7:29–33. - PubMed
-
- Bradford M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976;72:248–254. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

