Bacterial infection as assessed by in vivo gene expression
- PMID: 9023360
- PMCID: PMC19617
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.94.3.934
Bacterial infection as assessed by in vivo gene expression
Abstract
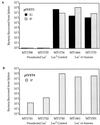
In vivo expression technology (IVET) has been used to identify > 100 Salmonella typhimurium genes that are specifically expressed during infection of BALB/c mice and/or murine cultured macrophages. Induction of these genes is shown to be required for survival in the animal under conditions of the IVET selection. One class of in vivo induced (ivi) genes, iviVI-A and iviVI-B, constitute an operon that resides in a region of the Salmonella genome with low G+C content and presumably has been acquired by horizontal transfer. These ivi genes encode predicted proteins that are similar to adhesins and invasins from prokaryotic and eukaryotic pathogens (Escherichia coli [tia], Plasmodium falciparum [PfEMP1]) and have coopted the PhoPQ regulatory circuitry of Salmonella virulence genes. Examination of the in vivo induction profile indicates (i) many ivi genes encode regulatory functions (e.g., phoPQ and pmrAB) that serve to enhance the sensitivity and amplitude of virulence gene expression (e.g., spvB); (ii) the biochemical function of many metabolic genes may not represent their sole contribution to virulence; (iii) the host ecology can be inferred from the biochemical functions of ivi genes; and (iv) nutrient limitation plays a dual signaling role in pathogenesis: to induce metabolic functions that complement host nutritional deficiencies and to induce virulence functions required for immediate survival and spread to subsequent host sites.
Figures
References
-
- Falkow S. In: Escherichia coli and Salmonella Cellular and Molecular Biology. 2nd Ed. Neidhardt F C, Curtiss R III, Ingraham J L, Lin E C C, Low K B, Magasanik B, Reznikoff W S, Riley M, Schaechter M, Umbarger H E, editors. Washington, DC: Am. Soc. Microbiol.; 1996. pp. 2723–2729.
-
- Mahan M J, Slauch J M, Mekalanos J J. Science. 1993;259:686–688. - PubMed
-
- Davis R W, Botstein D, Roth J R. Advanced Bacterial Genetics. Plainview, New York: Cold Spring Harbor Lab. Press; 1980.
-
- Schmieger H. Mol Gen Genet. 1972;119:75–88. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

