GKAP, a novel synaptic protein that interacts with the guanylate kinase-like domain of the PSD-95/SAP90 family of channel clustering molecules
- PMID: 9024696
- PMCID: PMC2134290
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.136.3.669
GKAP, a novel synaptic protein that interacts with the guanylate kinase-like domain of the PSD-95/SAP90 family of channel clustering molecules
Abstract
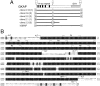
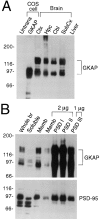
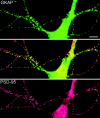
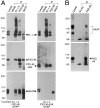
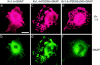
The molecular mechanisms underlying the organization of ion channels and signaling molecules at the synaptic junction are largely unknown. Recently, members of the PSD-95/SAP90 family of synaptic MAGUK (membrane-associated guanylate kinase) proteins have been shown to interact, via their NH2-terminal PDZ domains, with certain ion channels (NMDA receptors and K+ channels), thereby promoting the clustering of these proteins. Although the function of the NH2-terminal PDZ domains is relatively well characterized, the function of the Src homology 3 (SH3) domain and the guanylate kinase-like (GK) domain in the COOH-terminal half of PSD-95 has remained obscure. We now report the isolation of a novel synaptic protein, termed GKAP for guanylate kinase-associated protein, that binds directly to the GK domain of the four known members of the mammalian PSD-95 family. GKAP shows a unique domain structure and appears to be a major constituent of the postsynaptic density. GKAP colocalizes and coimmunoprecipitates with PSD-95 in vivo, and coclusters with PSD-95 and K+ channels/NMDA receptors in heterologous cells. Given their apparent lack of guanylate kinase enzymatic activity, the fact that the GK domain can act as a site for protein-protein interaction has implications for the function of diverse GK-containing proteins (such as p55, ZO-1, and LIN-2/CASK).
Figures



References
-
- Anderson JM. Cell signalling-MAGUK magic. Curr Biol. 1996;6:382–384. - PubMed
-
- Banker GA, Cowan WM. Rat hippocampal neurons in dispersed cell culture. Brain Res. 1977;126:397–425. - PubMed
-
- Bartel, P.L., C.-T. Chien, R. Sternglanz, and S. Fields. 1993. Using the 2-hybrid system to detect protein-protein interactions. In Cellular Interactions in Development: A Practical Approach, Oxford University Press, Oxford. 153– 179.
-
- Brenman JE, Chao DS, Gee SH, McGee AW, Craven SE, Santillano DR, Wu Z, Huang F, Xia H, Peters MF, et al. Interaction of nitric oxide synthase with the postsynaptic density protein PSD-95 and α1-syntrophin mediated by PDZ domains. Cell. 1996;84:757–767. - PubMed
-
- Cho K-O, Hunt CA, Kennedy MB. The rat brain postsynaptic density fraction contains a homolog of the drosophila discs-large tumor suppressor protein. Neuron. 1992;9:929–942. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

