IgE enhances mouse mast cell Fc(epsilon)RI expression in vitro and in vivo: evidence for a novel amplification mechanism in IgE-dependent reactions
- PMID: 9034145
- PMCID: PMC2196143
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.185.4.663
IgE enhances mouse mast cell Fc(epsilon)RI expression in vitro and in vivo: evidence for a novel amplification mechanism in IgE-dependent reactions
Abstract
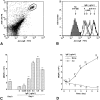
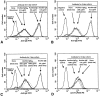
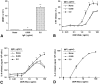
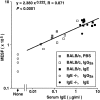
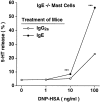
The binding of immunoglobulin E (IgE) to high affinity IgE receptors (Fc(epsilon)RI) expressed on the surface of mast cells primes these cells to secrete, upon subsequent exposure to specific antigen, a panel of proinflammatory mediators, which includes cytokines that can also have immunoregulatory activities. This IgE- and antigen-specific mast cell activation and mediator production is thought to be critical to the pathogenesis of allergic disorders, such as anaphylaxis and asthma, and also contributes to host defense against parasites. We now report that exposure to IgE results in a striking (up to 32-fold) upregulation of surface expression of Fc(epsilon)RI on mouse mast cells in vitro or in vivo. Moreover, baseline levels of Fc(epsilon)RI expression on peritoneal mast cells from genetically IgE-deficient (IgE -/-) mice are dramatically reduced (by approximately 83%) compared with those on cells from the corresponding normal mice. In vitro studies indicate that the IgE-dependent upregulation of mouse mast cell Fc(epsilon)RI expression has two components: an early cycloheximide-insensitive phase, followed by a later and more sustained component that is highly sensitive to inhibition by cycloheximide. In turn, IgE-dependent upregulation of Fc(epsilon)RI expression significantly enhances the ability of mouse mast cells to release serotonin, interleukin-6 (IL-6), and IL-4 in response to challenge with IgE and specific antigen. The demonstration that IgE-dependent enhancement of mast cell Fc(epsilon)RI expression permits mast cells to respond to antigen challenge with increased production of proinflammatory and immunoregulatory mediators provides new insights into both the pathogenesis of allergic diseases and the regulation of protective host responses to parasites.
Figures
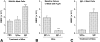



References
-
- Ishizaka T, Ishizaka K. Activation of mast cells for mediator release through IgE receptors. Prog Allergy. 1984;34:188–235. - PubMed
-
- Jarrett, E.E.E., and H.R.P. Miller. 1982. Production and activities of IgE in helminth infection. In Progress in Allergy. Vol. 31: Immunity and Concomitant Immunity in Infectious Diseases. P. Kallós, volume editor. S. Karger, Basel. 178–233. - PubMed
-
- Matsuda H, Watanabe N, Kiso Y, Hirota S, Ushio H, Kannan Y, Azuma M, Koyama H, Kitamura Y. Necessity of IgE antibodies and mast cells for manifestation of resistance against larval Haemaphysalis longicornisticks in mice. J Immunol. 1990;144:259–262. - PubMed
-
- Bochner BS, Lichtenstein LM. Anaphylaxis. N Engl J Med. 1991;324:1785–1790. - PubMed
-
- Ravetch JV, Kinet J-P. Fc receptors. Annu Rev Immunol. 1991;9:457–492. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

