A bacterial basic region leucine zipper histidine kinase regulating toluene degradation
- PMID: 9037074
- PMCID: PMC19812
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.94.4.1453
A bacterial basic region leucine zipper histidine kinase regulating toluene degradation
Abstract
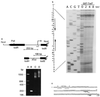
The two-component signal transduction pathways in bacteria use a histidine-aspartate phosphorelay circuit to mediate cellular changes in response to environmental stimuli. Here we describe a novel two-component todST system, which activates expression of the toluene degradation (tod) pathway in Pseudomonas putida F1. The todS gene is predicted to encode a sensory hybrid kinase with two unique properties--a basic region leucine zipper dimerization motif at the N terminus and a duplicated histidine kinase motif. Evidence from a synthetic peptide model suggests that TodS binds as a dimer to a pseudopalindromic sequence (5'-TGACTCA), which resembles the recognition sequence of the eukaryotic transcription factors Fos and Jun. These results provide additional evidence that bacteria and eukaryotes share common regulatory motifs. The todT gene product, a response regulator, was overproduced as a fusion protein in Escherichia coli, and the purified protein was found to bind specifically to a 6-bp palindromic DNA structure in the tod control region. The phosphorylated form of TodT appears to be the activator of tod structural genes. This is the first report of a two-component system that regulates aromatic metabolism in bacteria.
Figures



References
-
- Zylstra G J, Gibson D T. In: Genetic Engineering: Principles and Methods. Setlow J K, editor. Vol. 13. New York: Plenum; 1991. pp. 183–203. - PubMed
-
- Finette B A, Gibson D T. Biocatalysis. 1988;2:29–37.
-
- Parkinson J S, Kofoid E C. Annu Rev Genet. 1992;26:71–112. - PubMed
-
- Hoch J A, Silhavy T J. Two-Component Signal Transduction. Washington, DC: Am. Soc. Microbiol.; 1995.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

