The MUR1 gene of Arabidopsis thaliana encodes an isoform of GDP-D-mannose-4,6-dehydratase, catalyzing the first step in the de novo synthesis of GDP-L-fucose
- PMID: 9050909
- PMCID: PMC20047
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.94.5.2085
The MUR1 gene of Arabidopsis thaliana encodes an isoform of GDP-D-mannose-4,6-dehydratase, catalyzing the first step in the de novo synthesis of GDP-L-fucose
Abstract
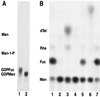
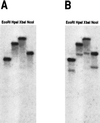
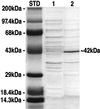
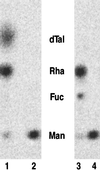
GDP-L-fucose is the activated nucleotide sugar form of L-fucose, which is a constituent of many structural polysaccharides and glycoproteins in various organisms. The de novo synthesis of GDP-L-fucose from GDP-D-mannose encompasses three catalytic steps, a 4,6-dehydration, a 3,5-epimerization, and a 4-reduction. The mur1 mutant of Arabidopsis is deficient in L-fucose in the shoot and is rescued by growth in the presence of exogenously supplied L-fucose. Biochemical assays of the de novo pathway for the synthesis of GDP-L-fucose indicated that mur1 was blocked in the first nucleotide sugar interconversion step, a GDP-D-mannose-4,6-dehydratase. An expressed sequence tag was identified that showed significant sequence similarity to proposed bacterial GDP-D-mannose-4,6-dehydratases and was tightly linked to the mur1 locus. A full-length clone was isolated from a cDNA library, and its coding region was expressed in Escherichia coli. The recombinant protein exhibited GDP-D-mannose-4,6-dehydratase activity in vitro and was able to complement mur1 extracts in vitro to complete the pathway for the synthesis of GDP-L-fucose. All seven mur1 alleles investigated showed single point mutations in the coding region for the 4,6-dehydratase, confirming that it represents the MUR1 gene.
Figures



References
-
- Levy S, York W S, Stuike-Prill R, Meyer B, Staehelin L A. Plant J. 1991;1:195–215. - PubMed
-
- Ginsburg V. J Biol Chem. 1961;236:2389–2393. - PubMed
-
- Markovitz A. J Biol Chem. 1964;239:2091–2098. - PubMed
-
- Feingold D S, Avigad G. In: The Biochemistry of Plants: A Comprehensive Treatise. Stumpf P K, Conn E E, editors. Vol. 3. New York: Academic; 1980. pp. 101–170.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

