Viral superantigen drives extrafollicular and follicular B cell differentiation leading to virus-specific antibody production
- PMID: 9053455
- PMCID: PMC2196032
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.185.3.551
Viral superantigen drives extrafollicular and follicular B cell differentiation leading to virus-specific antibody production
Abstract
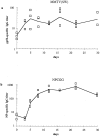
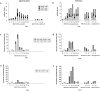
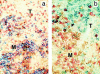
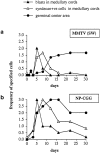
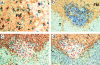
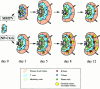
Mouse mammary tumor virus (MMTV[SW]) encodes a superantigen expressed by infected B cells. It evokes an antibody response specific for viral envelope protein, indicating selective activation of antigen-specific B cells. The response to MMTV(SW) in draining lymph nodes was compared with the response to haptenated chicken gamma globulin (NP-CGG) using flow cytometry and immunohistology. T cell priming occurs in both responses, with T cells proliferating in association with interdigitating dendritic cells in the T zone. T cell proliferation continues in the presence of B cells in the outer T zone, and B blasts then undergo exponential growth and differentiation into plasma cells in the medullary cords. Germinal centers develop in both responses, but those induced by MMTV(SW) appear later and are smaller. Most T cells activated in the T zone and germinal centers in the MMTV(SW) response are superantigen specific and these persist for weeks in lymph nodes draining the site MMTV(SW) injection: this contrasts with the selective loss of superantigen-specific T cells from other secondary lymphoid tissues. The results indicate that this viral superantigen, when expressed by professional antigen-presenting cells, drives extrafollicular and follicular B cell differentiation leading to virus-specific antibody production.
Figures
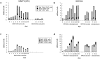

References
-
- Acha-Orbea H, MacDonald HR. Superantigens of mouse mammary tumor virus. Annu Rev Immunol. 1995;13:459–486. - PubMed
-
- Held W, Waanders GA, Shakhov AN, Scarpellino L, Acha-Orbea H, MacDonald HR. Superantigeninduced immune stimulation amplifies mouse mammary tumor virus infection and allows virus transmission. Cell. 1993;74:529–540. - PubMed
-
- Webb S, Morris C, Sprent J. Extrathymic tolerance of mature T cells: clonal elimination as a consequence of immunity. Cell. 1990;63:1249–1256. - PubMed
-
- Kawabe Y, Ochi A. Programmed cell-death and extrathymic reduction of Vβ8+ CD4+T cells in mice tolerant to staphylococcus aureus enterotoxin B. Nature (Lond) 1991;349:245–248. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

