Purinergic modulation of interleukin-1 beta release from microglial cells stimulated with bacterial endotoxin
- PMID: 9053458
- PMCID: PMC2196027
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.185.3.579
Purinergic modulation of interleukin-1 beta release from microglial cells stimulated with bacterial endotoxin
Abstract
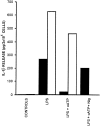
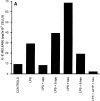
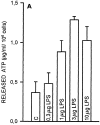
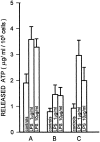
Microglial cells express a peculiar plasma membrane receptor for extracellular ATP, named P2Z/P2X7 purinergic receptor, that triggers massive transmembrane ion fluxes and a reversible permeabilization of the plasma membrane to hydrophylic molecules of up to 900 dalton molecule weight and eventual cell death (Di Virgilio, F. 1995. Immunol. Today, 16:524-528). The physiological role of this newly cloned (Surprenant, A., F. Rassendren, E. Kawashima, R. A. North and G. Buell, 1996. Science (Wash. DC). 272:735-737) cytolytic receptor is unknown. In vitro and in vivo activation of the macrophage and microglial cell P2Z/P2X7 receptor by exogenous ATP causes a large and rapid release of mature IL-1 beta. In the present report we investigated the role of microglial P2Z/P2X7 receptor in IL-1 beta release triggered by LPS. Our data suggest that LPS-dependent IL-1 beta release involves activation of this purinergic receptor as it is inhibited by the selective P2Z/P2X7 blocker oxidized ATP and modulated by ATP-hydrolyzing enzymes such as apyrase or hexokinase. Furthermore, microglial cells release ATP when stimulated with LPS. LPS-dependent release of ATP is also observed in monocyte-derived human macrophages. It is suggested that bacterial endotoxin activates an autocrine/paracrine loop that drives ATP-dependent IL-1 beta secretion.
Figures


References
-
- Surprenant A, Rassendren F, Kawashima E, North RA, Buell G. The cytolytic P2Z receptor for extracellular ATP identified as a P2X receptor (P2X7) Science (Wash DC) 1996;272:735–738. - PubMed
-
- Ferrari D, Villalba M, Chiozzi P, Falzoni S, RicciardiCastagnoli P, Di Virgilio F. Mouse microglial cells express a plasma membrane pore gated by extracellular ATP. J Immunol. 1996;156:1531–1539. - PubMed
-
- Zimmermann H. Signalling via ATP in the nervous system. Trends Neurosci. 1994;17:420–426. - PubMed
-
- Dinarello CA. Interleukin-1. Rev Infect Dis. 1984;6:51–95. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

