Distribution of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) protein and mRNA in the normal adult rat CNS: evidence for anterograde axonal transport
- PMID: 9065491
- PMCID: PMC6573520
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.17-07-02295.1997
Distribution of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) protein and mRNA in the normal adult rat CNS: evidence for anterograde axonal transport
Abstract
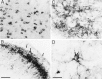
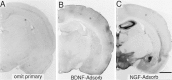
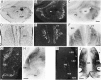
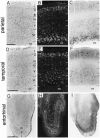
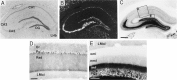
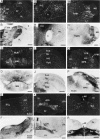
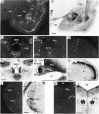
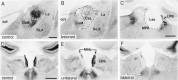
A sensitive immunohistochemical technique was used, along with highly specific affinity-purified antibodies to brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), to generate a detailed mapping of BDNF immunoreactivity (BDNF-ir) throughout the adult rat CNS. A parallel analysis of sites of BDNF synthesis was performed with in situ hybridization techniques using a cRNA probe to the exon encoding mature rat BDNF protein. These combined data revealed (1) groups of cell bodies containing diffuse BDNF-ir throughout the CNS that were strongly correlated with fields of cells containing BDNF mRNA; (2) varying degrees of BDNF-ir outside of cell bodies, in what appeared to be fibers and/or terminals; and (3) many regions containing extremely heavy BDNF-immunoreactive fiber/terminal labeling that lacked BDNF mRNA (e.g., medial habenula, central nucleus of the amygdala, bed nucleus of stria terminalis, lateral septum, and spinal cord). The latter observation suggested that in these regions BDNF was derived from anterograde axonal transport by afferent systems. In the two cases in which this hypothesis was tested by the elimination of select afferents, BDNF immunostaining was completely eliminated. These data, along with the observation that BDNF-ir was rarely found within dendrites or fibers en passage, suggest that BDNF protein produced in adult CNS neurons is polarized primarily along axonal processes and is preferentially stored in terminals within the innervation target.
Figures


References
-
- Alden M, Besson J-M, Bernard J-F. Organization of the efferent projections from the pontine parabrachial area to the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis and neighboring regions: a PHA-L study in the rat. J Comp Neurol. 1994;341:289–314. - PubMed
-
- Berkemeier LR, Winslow JW, Kaplan DR, Nikolics K, Goeddel DV, Rosenthal A. Neurotrophin-5: a novel neurotrophic factor that activates trk and trkB. Neuron. 1991;7:857–866. - PubMed
-
- Bernard J-F, Alden M, Besson J-M. The organization of the efferent projections from the pontine parabrachial area to the amygdaloid complex: a phaseolus vulgaris leucoagglutinin (PHA-L) study in the rat. J Comp Neurol. 1993;329:201–229. - PubMed
-
- Blöchl A, Thoenen H. Characterization of nerve growth factor (NGF) release from hippocampal neurons: evidence for a constitutive and an unconventional sodium-dependent regulated pathway. Eur J Neurosci. 1995;7:1220–1228. - PubMed
-
- Blöchl A, Thoenen H. Localization of cellular storage compartments and sites of constitutive and activity-dependent release of nerve growth factor (NGF) in primary cultures of hippocampal neurons. Mol Cell Neurosci. 1996;7:173–190. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
