Environmental knowledge is subserved by separable dorsal/ventral neural areas
- PMID: 9065511
- PMCID: PMC6573507
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.17-07-02512.1997
Environmental knowledge is subserved by separable dorsal/ventral neural areas
Abstract
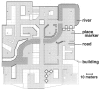
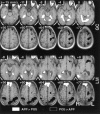
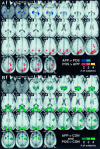
Environmental psychology models propose that knowledge of large-scale space is stored as distinct landmark (place appearance) and survey (place position) information. Studies of brain-damaged patients suffering from "topographical disorientation" tentatively support this proposal. In order to determine if the components of psychologically derived models of environmental representation are realized as distinct functional, neuroanatomical regions, a functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) study of environmental knowledge was performed. During scanning, subjects made judgments regarding the appearance and position of familiar locations within a virtual reality environment. The fMRI data were analyzed in a manner that has been empirically demonstrated to rigorously control type I error and provide optimum sensitivity, allowing meaningful results in the single subject. A direct comparison of the survey position and landmark appearance conditions revealed a dorsal/ventral dissociation in three of four subjects. These results are discussed in the context of the observed forms of topographical disorientation and are found to be in good agreement with the human lesion studies. This experiment confirms that environmental knowledge is not represented by a unitary system but is instead functionally distributed across the neocortex.
Figures

References
-
- Aguirre GK, Detre JA, Alsop DC, D’Esposito M. The parahippocampus subserves topographical learning in man. Cereb Cortex. 1996;6:823–829. - PubMed
-
- Aguirre GK, Zarahn E, D’Esposito M (1997) Empirical analyses of BOLD fMRI statistics. II. Spatially smoothed data collected under null-hypothesis and experimental conditions. NeuroImage, in press. - PubMed
-
- Allison T, Ginter H, McCarthy G, Nobre AC, Puce A, Luby M, Spencer DD. Face recognition in human extrastriate cortex. J Neurophysiol. 1994;71:821–825. - PubMed
-
- Bottini G, Cappa S, Geminiani G, Sterzi R. Topographic disorientation: a case report. Neuropsychologia. 1990;28:309–312. - PubMed
-
- Cohen JD, MacWhinney M, Flatt M, Provost J. PsyScope: a new graphic interactive environment for designing psychology experiments. Behav Res Methods Instrum Comput. 1993;25:257–271.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
