mu-Opioid receptors are localized to extrasynaptic plasma membranes of GABAergic neurons and their targets in the rat nucleus accumbens
- PMID: 9065518
- PMCID: PMC6573510
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.17-07-02585.1997
mu-Opioid receptors are localized to extrasynaptic plasma membranes of GABAergic neurons and their targets in the rat nucleus accumbens
Abstract
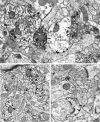
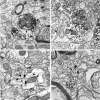
The activation of mu-opioid receptors in the nucleus accumbens (Acb) produces changes in locomotor and rewarding responses that are believed to involve neurons, including local gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA)ergic neurons. We combined immunogold-silver detection of an antipeptide antiserum against the cloned mu-opioid receptor (MOR) and immunoperoxidase labeling of an antibody against GABA to determine the cellular basis for the proposed opioid modulation of GABAergic neurons in the rat Acb. MOR-like immunoreactivity (MOR-LI) was localized prominently to plasma membranes of neurons having morphological features of both spiny and aspiny cells, many of which contained GABA. Of 351 examples of profiles that contained MOR-LI and GABA labeling, 65% were dendrites. In these dendrites, MOR-LI was seen mainly along extrasynaptic portions of the plasma membrane apposed to unlabeled terminals and/or glial processes. Dually labeled dendrites often received convergent input from GABAergic terminals and/or from unlabeled terminals forming asymmetric excitatory-type synapses. Of all profiles that contained both MOR and GABA immunoreactivity, 28% were axon terminals. MOR-containing GABAergic terminals and terminals separately labeled for MOR or GABA formed synapses with unlabeled dendrites and also with dendrites containing MOR or GABA. Our results indicate that MOR agonists could modulate the activity of GABA neurons in the Acb via receptors located mainly at extrasynaptic sites on dendritic plasma membranes. MOR ligands also could alter the release of GABA onto target dendrites that contain GABA and/or respond to opiate stimulation.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Dual ultrastructural localization of mu-opioid receptors and NMDA-type glutamate receptors in the shell of the rat nucleus accumbens.J Neurosci. 1997 Jun 15;17(12):4839-48. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.17-12-04839.1997. J Neurosci. 1997. PMID: 9169542 Free PMC article.
-
Ultrastructural immunocytochemical localization of mu-opioid receptors in rat nucleus accumbens: extrasynaptic plasmalemmal distribution and association with Leu5-enkephalin.J Neurosci. 1996 Jul 1;16(13):4162-73. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.16-13-04162.1996. J Neurosci. 1996. PMID: 8753878 Free PMC article.
-
Mu opioid receptors are in somatodendritic and axonal compartments of GABAergic neurons in rat hippocampal formation.Brain Res. 1999 Dec 4;849(1-2):203-15. doi: 10.1016/s0006-8993(99)01910-1. Brain Res. 1999. PMID: 10592303
-
Ultrastructural localization of mu-opioid receptors in the superficial layers of the rat cervical spinal cord: extrasynaptic localization and proximity to Leu5-enkephalin.Brain Res. 1996 Aug 26;731(1-2):141-54. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(96)00492-1. Brain Res. 1996. PMID: 8883864
-
Ultrastructural immunocytochemical localization of mu opioid receptors and Leu5-enkephalin in the patch compartment of the rat caudate-putamen nucleus.J Comp Neurol. 1996 Nov 25;375(4):659-74. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-9861(19961125)375:4<659::AID-CNE7>3.0.CO;2-0. J Comp Neurol. 1996. PMID: 8930791
Cited by
-
Pseudoginsenoside-F11 inhibits methamphetamine-induced behaviors by regulating dopaminergic and GABAergic neurons in the nucleus accumbens.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2016 Mar;233(5):831-40. doi: 10.1007/s00213-015-4159-8. Epub 2015 Dec 1. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2016. PMID: 26621348
-
A Discrete Presynaptic Vesicle Cycle for Neuromodulator Receptors.Neuron. 2020 Feb 19;105(4):663-677.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2019.11.016. Epub 2019 Dec 11. Neuron. 2020. PMID: 31837915 Free PMC article.
-
Cocaine and heroin ('speedball') self-administration: the involvement of nucleus accumbens dopamine and mu-opiate, but not delta-opiate receptors.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2005 Jun;180(1):21-32. doi: 10.1007/s00213-004-2135-9. Epub 2005 Jan 29. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2005. PMID: 15682301
-
Enhanced dendritic availability of μ-opioid receptors in inhibitory neurons of the extended amygdala in mice deficient in the corticotropin-releasing factor-1 receptor.Synapse. 2011 Jan;65(1):8-20. doi: 10.1002/syn.20810. Synapse. 2011. PMID: 20506149 Free PMC article.
-
mu-Opioid receptors and limbic responses to aversive emotional stimuli.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002 May 14;99(10):7084-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.102174799. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002. PMID: 12011464 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aronin N, DiFiglia M, Graveland GA, Schwartz WJ, Wu J-Y. Localization of immunoreactive enkephalins in GABA synthesizing neurons of the rat neostriatum. Brain Res. 1984;300:376–380. - PubMed
-
- Bausch SB, Patterson TA, Ehrengruber MU, Lester HA, Davidson N, Chavkin C. Colocalization of mu opioid receptors with GIRK1 potassium channels in the rat brain: an immunocytochemical study. Receptors Channels. 1995;3:221–241. - PubMed
-
- Bayer VE, Pickel VM. GABA-labeled terminals form proportionally more synapses with dopaminergic neurons having low densities of tyrosine hydroxylase immunoreactivity in rat ventral tegmental area. Brain Res. 1991;559:44–55. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
