Genetic analysis of myoblast fusion: blown fuse is required for progression beyond the prefusion complex
- PMID: 9087441
- PMCID: PMC2132517
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.136.6.1249
Genetic analysis of myoblast fusion: blown fuse is required for progression beyond the prefusion complex
Abstract
The events of myoblast fusion in Drosophila are dissected here by combining genetic analysis with light and electron microscopy. We describe a new and essential intermediate step in the process, the formation of a prefusion complex consisting of "paired vesicles." These pairs of vesicles from different cells align with each other across apposed plasma membranes. This prefusion complex resolves into dense membrane plaques between apposed cells; these cells then establish cytoplasmic continuity by fusion of small areas of plasma membrane followed by vesiculation of apposed membranes. Different steps in this process are specifically blocked by mutations in four genes required for myoblast fusion. One of these genes, blown fuse, encodes a novel cytoplasmic protein expressed in unfused myoblasts that is essential for progression beyond the prefusion complex stage.
Figures

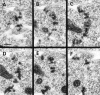


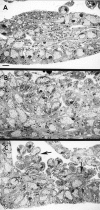
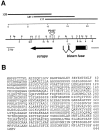


References
-
- Abmayr SM, Erickson MS, Bour BA. Embryonic development of the larval body wall musculature of Drosophila melanogaster. . Trends Genet. 1995;11:153–159. - PubMed
-
- Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990;215:403–410. - PubMed
-
- Ball EE, Goodman CS. Muscle development in the grasshopper embryo: II. Syncytial origin of the extensor tibiae muscle pioneers. Dev Biol. 1985a;111:399–416. - PubMed
-
- Ball EE, Goodman CS. Muscle development in the grasshopper embryo: III. Sequential origin of the flexor tibiae muscle pioneers. Dev Biol. 1985b;111:417–424. - PubMed
-
- Ball EE, Ho RK, Goodman CS. Muscle development in the grasshopper embryo. I. Muscles, nerves and apodemes in the metathoracic leg. Dev Biol. 1985c;111:383–398. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

