The human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) Vpu protein interferes with an early step in the biosynthesis of major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I molecules
- PMID: 9104816
- PMCID: PMC2196253
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.185.7.1295
The human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) Vpu protein interferes with an early step in the biosynthesis of major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I molecules
Abstract
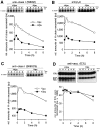
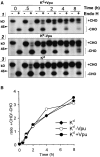
The human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) vpu gene encodes a small integral membrane phosphoprotein with two established functions: degradation of the viral coreceptor CD4 in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and augmentation of virus particle release from the plasma membrane of HIV-1-infected cells. We show here that Vpu is also largely responsible for the previously observed decrease in the expression of major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I molecules on the surface of HIV-1-infected cells. Cells infected with HIV-1 isolates that fail to express Vpu, or that express genetically modified forms of Vpu that no longer induce CD4 degradation, exhibit little downregulation of MHC class I molecules. The effect of Vpu on class I biogenesis was analyzed in more detail using a Vpu-expressing recombinant vaccinia virus (VV). VV-expressed Vpu induces the rapid loss of newly synthesized endogenous or VV-expressed class I heavy chains in the ER, detectable either biochemically or by reduced cell surface expression. This effect is of similar rapidity and magnitude as the VV-expressed Vpu-induced degradation of CD4. Vpu had no discernible effects on cell surface expression of VV-expressed mouse CD54, demonstrating the selectivity of its effects on CD4 and class I heavy chains. VV-expressed Vpu does not detectably affect class I molecules that have been exported from the ER. The detrimental effects of Vpu on class I molecules could be distinguished from those caused by VV-expressed herpes virus protein ICP47, which acts by decreasing the supply of cytosolic peptides to class I molecules, indicating that Vpu functions in a distinct manner from ICP47. Based on these findings, we propose that Vpu-induced downregulation of class I molecules may be an important factor in the evolutionary selection of the HIV-1-specific vpu gene by contributing to the inability of CD8+ T cells to eradicate HIV-1 from infected individuals.
Figures












References
-
- Townsend A, Öhlén C, Bastin J, Ljunggren H-G, Foster L, Kärre K. Association of class I major histocompatibility heavy and light chains induced by viral peptides. Nature (Lond) 1989;340:443–448. - PubMed
-
- Yewdell JW, Bennink JR. Cell biology of antigen processing and presentation to MHC class I moleculerestricted T lymphocytes. Adv Immunol. 1992;52:1–23. - PubMed
-
- Heemels M-T, Ploegh H. Generation, translocation, and presentation of MHC class I–restricted peptides. Annu Rev Biochem. 1995;64:463–491. - PubMed
-
- Peters JM. Proteasomes: protein degradation machines of the cell. TIBS (Trends Biochem Sci) 1994;19:377–382. - PubMed
-
- Niedermann G, Butz S, Ihlenfeldt HG, Grimm R, Lucchiari M, Hoschützky H, Jung G, Maier B, Eichmann K. Contribution of proteasome-mediated proteolysis to the hierarchy of epitopes presented by major histocompatibility complex class I molecules. Immunity. 1995;2:289–299. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

