Mutagenic effects of a single and an exact number of alpha particles in mammalian cells
- PMID: 9108052
- PMCID: PMC20515
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.94.8.3765
Mutagenic effects of a single and an exact number of alpha particles in mammalian cells
Abstract
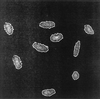
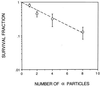
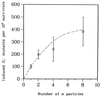
One of the main uncertainties in risk estimation for environmental radon exposure using lung cancer data from underground miners is the extrapolation from high- to low-dose exposure where multiple traversal is extremely rare. The biological effects of a single alpha particle are currently unknown. Using the recently available microbeam source at the Radiological Research Accelerator Facility at Columbia University, we examined the frequencies and molecular spectrum of S1- mutants induced in human-hamster hybrid (A(L)) cells by either a single or an exact number of alpha particles. Exponentially growing cells were stained briefly with a nontoxic concentration of Hoechst dye for image analysis, and the location of individual cells was computer-monitored. The nucleus of each cell was irradiated with either 1,2,4, or 8 alpha particles at a linear energy transfer of 90 keV/microm consistent with the energy spectrum of domestic radon exposure. Although single-particle traversal was only slightly cytotoxic to A(L) cells (survival fraction approximately 0.82), it was highly mutagenic, and the induced mutant fraction averaged 110 mutants per 10(5) survivors. In addition, both toxicity and mutant induction were dose-dependent. Multiplex PCR analysis of mutant DNA showed that the proportion of mutants with multilocus deletions increased with the number of particle traversals. These data provide direct evidence that a single a particle traversing a nucleus will have a high probability of resulting in a mutation and highlight the need for radiation protection at low doses.
Figures
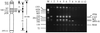

Comment in
-
What are the risks of low-level exposure to alpha radiation from radon?Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997 Jun 10;94(12):5996-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.94.12.5996. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997. PMID: 9177156 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
References
-
- National Council on Radiation Protection and Measurements. National Council on Radiation Protection and Measurements Report No. 79. Washington, DC: National Academy of Sciences; 1984.
-
- Lundin F E, Lloyd J W, Smith E M, Archer V E, Holaday D A. Health Phys. 1969;16:571–578. - PubMed
-
- Whittemore A S, McMillan A. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1983;71:489–493. - PubMed
-
- National Research Council Committee on Health Risks of Exposure to Radon (BEIR VI) Health Effects of Exposure to Radon: Time for Reassessment. Washington, DC: National Academy of Sciences; 1994.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

