Genetic determinants of susceptibility to excitotoxic cell death: implications for gene targeting approaches
- PMID: 9108112
- PMCID: PMC20575
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.94.8.4103
Genetic determinants of susceptibility to excitotoxic cell death: implications for gene targeting approaches
Abstract
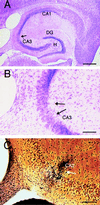
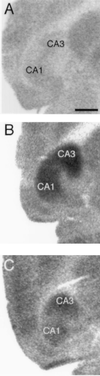
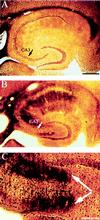
Recent studies have sought to identify the genes involved in excitotoxic neurodegeneration. Here we report that certain strains of mice, including strains that are used for gene targeting studies, do not exhibit excitotoxic cell death after kainic acid seizures. Kainic acid produced excitotoxic cell death in the CA3 and CA1 subfields of the hippocampus in 129/SvEMS and FVB/N mice, in the same pattern as described in rats. C57BL/6 and BALB/c mice exhibited excitotoxic cell death only at very high doses of kainate, and then only in a very restricted area, although they exhibited comparable seizures. Hybrids of 129/SvEMS x C57BL/6 mice created using embryonic stem cells from 129/SvEMS mice also did not exhibit excitotoxic cell death. These results demonstrate that C57BL/6 and BALB/c strains carry gene(s) that convey protection from glutamate-induced excitotoxicity. This differential susceptibility to excitotoxicity represents a potential complication for gene targeting studies.
Figures

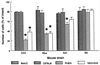
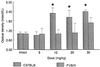
References
-
- A. A, Horrocks L A. Brain Res Rev. 1991;16:171–191. - PubMed
-
- Rothman S M, Olney J W. Trends Neurosci. 1987;10:299–302.
-
- Choi D W. Prog Brain Res. 1994;100:47–51. - PubMed
-
- Hori N, French-Mullen J H M, Carpenter D O. Brain Res. 1985;358:380–384. - PubMed
-
- Choi D W. Trends Neurosci. 1988;11:465–469. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

