Fertilization-independent seed development in Arabidopsis thaliana
- PMID: 9108133
- PMCID: PMC20611
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.94.8.4223
Fertilization-independent seed development in Arabidopsis thaliana
Abstract
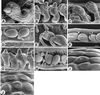
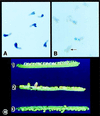
We report mutants in Arabidopsis thaliana (fertilization-independent seed:fis) in which certain processes of seed development are uncoupled from the double fertilization event that occurs after pollination. These mutants were isolated as ethyl methanesulfonate-induced pseudo-revertants of the pistillata phenotype. Although the pistillata (pi) mutant has short siliques devoid of seed, the fis mutants in the pi background have long siliques containing developing seeds, even though the flowers remain free of pollen. The three fis mutations map to loci on three different chromosomes. In fis1 and fis2 seeds, the autonomous endosperm nuclei are diploid and the endosperm develops to the point of cellularization; the partially developed seeds then atrophy. In these two mutants, proembryos are formed in a low proportion of seeds and do not develop beyond the globular stage. When FIS/fis plants are pollinated by pollen from FIS/FIS plants, approximately 50% of the resulting seeds contain fully developed embryos; these seeds germinate and form viable seedlings (FIS/FIS). The other 50% of seeds shrivel and do not germinate; they contain embryos arrested at the torpedo stage (FIS/fis). In normal sexual reproduction, the products of the FIS genes are likely to play important regulatory roles in the development of seed after fertilization.
Figures



References
-
- Peacock W J. Apomixis Newsletter. 1992;4:3–7.
-
- Asker S E, Jerling L. Apomixis in Plants. Boca Raton, FL: CRC; 1992.
-
- Peacock J, Ming L, Craig S, Dennis E, Chaudhury A. Induced Mutations and Molecular Techniques for Crop Improvement. Vienna: International Atomic Energy Agency; 1995. pp. 117–125.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

