Localization of guanylate cyclase-activating protein 2 in mammalian retinas
- PMID: 9114059
- PMCID: PMC20792
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.94.9.4727
Localization of guanylate cyclase-activating protein 2 in mammalian retinas
Abstract
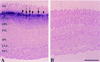
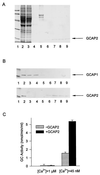
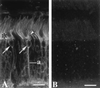
Guanylate cyclase-activating proteins (GCAP1 and GCAP2) are thought to mediate the intracellular stimulation of guanylate cyclase (GC) by Ca2+, a key event in recovery of the dark state of rod photoreceptors after exposure to light. GCAP1 has been localized to rod and cone outer segments, the sites of phototransduction, and to photoreceptor synaptic terminals and some cone somata. We used in situ hybridization and immunocytochemistry to localize GCAP2 in human, monkey, and bovine retinas. In human and monkey retinas, the most intense immunolabeling with anti-GCAP2 antibodies was in the cone inner segments, somata, and synaptic terminals and, to a lesser degree, in rod inner segments and inner retinal neurons. In bovine retina, the most intense immunolabeling was in the rod inner segments, with weaker labeling of cone myoids, somata, and synapses. By using a GCAP2-specific antibody in enzymatic assays, we confirmed that GCAP1 but not GCAP2 is the major component that stimulates GC in bovine rod outer segment homogenates. These results suggest that although GCAP1 is involved in the Ca2+-sensitive regulation of GC in rod and cone outer segments, GCAP2 may have non-phototransduction functions in photoreceptors and inner retinal neurons.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The localization of guanylyl cyclase-activating proteins in the mammalian retina.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1998 Jun;39(7):1243-50. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1998. PMID: 9620085
-
Gene array and expression of mouse retina guanylate cyclase activating proteins 1 and 2.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1998 May;39(6):867-75. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1998. PMID: 9579466
-
Guanylate-cyclase-inhibitory protein is a frog retinal Ca2+-binding protein related to mammalian guanylate-cyclase-activating proteins.Eur J Biochem. 1998 Mar 15;252(3):591-9. doi: 10.1046/j.1432-1327.1998.2520591.x. Eur J Biochem. 1998. PMID: 9546678
-
Guanylate cyclase-activating proteins: structure, function, and diversity.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004 Oct 1;322(4):1123-30. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2004.07.122. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004. PMID: 15336959 Review.
-
Mouse models to study GCAP functions in intact photoreceptors.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2002;514:361-88. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-0121-3_22. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2002. PMID: 12596933 Review.
Cited by
-
Calcium-sensitive particulate guanylyl cyclase as a modulator of cAMP in olfactory receptor neurons.J Neurosci. 1998 May 1;18(9):3195-205. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.18-09-03195.1998. J Neurosci. 1998. PMID: 9547228 Free PMC article.
-
Diversity of guanylate cyclase-activating proteins (GCAPs) in teleost fish: characterization of three novel GCAPs (GCAP4, GCAP5, GCAP7) from zebrafish (Danio rerio) and prediction of eight GCAPs (GCAP1-8) in pufferfish (Fugu rubripes).J Mol Evol. 2004 Aug;59(2):204-217. doi: 10.1007/s00239-004-2614-y. J Mol Evol. 2004. PMID: 15486694 Free PMC article.
-
Guanylate cyclases and associated activator proteins in retinal disease.Mol Cell Biochem. 2010 Jan;334(1-2):157-68. doi: 10.1007/s11010-009-0331-y. Epub 2009 Nov 26. Mol Cell Biochem. 2010. PMID: 19941038 Review.
-
EF hand-mediated Ca- and cGMP-signaling in photoreceptor synaptic terminals.Front Mol Neurosci. 2012 Feb 29;5:26. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2012.00026. eCollection 2012. Front Mol Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22393316 Free PMC article.
-
Normal GCAPs partly compensate for altered cGMP signaling in retinal dystrophies associated with mutations in GUCA1A.Sci Rep. 2019 Dec 27;9(1):20105. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-56606-5. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31882816 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

