Bacterial lipopolysaccharide rapidly inhibits expression of C-C chemokine receptors in human monocytes
- PMID: 9120403
- PMCID: PMC2196159
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.185.5.969
Bacterial lipopolysaccharide rapidly inhibits expression of C-C chemokine receptors in human monocytes
Abstract
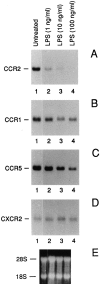
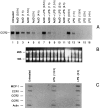
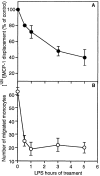
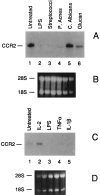
The present study was designed to investigate the effect of bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS) on C-C chemokine receptors (CCR) expressed in human mononuclear phagocytes. LPS caused a rapid and drastic reduction of CCR2 mRNA levels, which binds MCP-1 and -3. CCR1 and CCR5 mRNAs were also reduced, though to a lesser extent, whereas CXCR2 was unaffected. The rate of nuclear transcription of CCR2 was not affected by LPS, whereas the mRNA half life was reduced from 1.5 h to 45 min. As expected, LPS-induced inhibition of CCR2 mRNA expression was associated with a reduction of both MCP-1 binding and chemotactic responsiveness. The capacity to inhibit CCR2 expression in monocytes was shared by other microbial agents and cytokines (inactivated Streptococci, Propionibacterium acnes, and to a lesser extent, IL-1 and TNF-alpha). In contrast, IL-2 augmented CCR2 expression and MCP-1 itself had no effect. These results suggest that, regulation of receptor expression in addition to agonist production is likely a crucial point in the regulation of the chemokine system.
Figures
References
-
- Mantovani A, Bussolino F, Dejana E. Cytokine regulation of endothelial cell function. FASEB J. 1992;6:2591–2599. - PubMed
-
- Butcher EC. Leukocyte-endothelial cell recognition: three (or more) steps to specificity and diversity. Cell. 1991;67:1033–1036. - PubMed
-
- Springer TA. Traffic signal for lymphocyte recirculation and leukocyte emigration: the mutistep paradigm. Cell. 1994;76:301–314. - PubMed
-
- Baggiolini M, Dewald B, Moser B. Interleukin-8 and related chemotactic cytokines—CXC and CC chemokines. Adv Immunol. 1994;55:99–179. - PubMed
-
- Miller MD, Krangel MS. Biology and biochemistry of the chemokines: a family of chemotactic and inflammatory cytokines. Crit Rev Immunol. 1992;12:17–46. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

