Volatile signals of the major histocompatibility complex in male mouse urine
- PMID: 9122173
- PMCID: PMC20066
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.94.6.2210
Volatile signals of the major histocompatibility complex in male mouse urine
Abstract
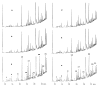
Variation in the genes of the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) contributes to unique individual odors (odortypes) in mice, as demonstrated by the ability of trained mice in a Y-maze olfactometer to discriminate nearly identical inbred mice that differ genetically only at the MHC (MHC congenic mice), while they cannot distinguish genetically identical inbred mice. Similar distinctions are possible with urine, a substance that is involved in many facets of mouse chemical communication. This paper reports results supporting the hypothesis that the MHC-determined urinary odor is composed of a mixture of volatile carboxylic acids occurring in relative concentrations that are characteristic of the odortype. Y-maze behavioral testing of urine fractions from anion exchange chromatography indicates that volatile acids are necessary and sufficient to convey MHC odortype information. Diethyl ether extracts, which are expected to contain the more volatile, less polar organic acids, were also discriminable in the Y-maze olfactometer. Ether extracts of 12 different urine samples from each of two panels of MHC congenic mice were analyzed by gas chromatography. No compounds unique to urine of either genotype were detected, but compounds did appear to occur in characteristic ratios in most of the samples of each type. Nonparametric statistical analysis of the gas chromatographic data showed that eight of the peaks occurred in significantly different relative concentrations in the congenic samples. One of the peaks was shown to represent phenylacetic acid, which has implications for the mechanism of the MHC specification of odortype.
Figures
References
-
- Klein J. Natural History of the Major Histocompatibility Complex. New York: Wiley; 1986.
-
- Potts W K, Wakeland E K. Trends Genet. 1993;9:408–412. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials