Molecular characterization of human and mouse fatty acid amide hydrolases
- PMID: 9122178
- PMCID: PMC20071
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.94.6.2238
Molecular characterization of human and mouse fatty acid amide hydrolases
Abstract
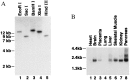
Recently, we reported the isolation, cloning, and expression of a rat enzyme, fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH), that degrades bioactive fatty acid amides like oleamide and anandamide to their corresponding acids, thereby serving to terminate the signaling functions of these molecules. Here, we report the molecular characterization of both a mouse and a human FAAH and compare these enzymes to the rat FAAH. The enzymes are well conserved in primary structure, with the mouse and rat FAAHs sharing 91% amino acid identity and the human FAAH sharing 82% and 84% identity with the rat FAAH and mouse FAAH, respectively. In addition, the expressed human and rat FAAHs behave biochemically as membrane proteins of comparable molecular size and show similar, but distinguishable, enzymological properties. The identification of highly homologous FAAH proteins in rat, mouse, and human supports a general role for the fatty acid amides in mammalian biology.
Figures


References
-
- Cravatt B F, Prospero-Garcia O, Siuzdak G, Gilula N B, Henriksen S J, Boger D L, Lerner R A. Science. 1995;268:1506–1509. - PubMed
-
- Devane W A, Hanus L, Breuer A, Pertwee R G, Stevenson L A, Griffin G, Gibson D, Mandelbaum A, Etinger A, Mechoulam R. Science. 1992;258:1946–1949. - PubMed
-
- Wakamatsu K, Masaki T, Itoh F, Koichi K, Sudo K. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990;168:423–429. - PubMed
-
- Barg J, Fride E, Hanus L, Levy R, Matus-Leibovitch N, Heldman E, Bayewitch M, Mechoulam R, Vogel Z. Eur J Pharmacol. 1995;287:145–152. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

