The p20 and Ded1 proteins have antagonistic roles in eIF4E-dependent translation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
- PMID: 9144215
- PMCID: PMC24656
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.94.10.5201
The p20 and Ded1 proteins have antagonistic roles in eIF4E-dependent translation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Abstract
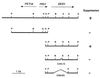
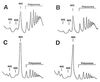
The translation initiation factor eIF4E mediates the binding of the small ribosomal subunit to the cap structure at the 5' end of the mRNA. In Saccharomyces cerevisiae, the cap-binding protein eIF4E is mainly associated with eIF4G, forming the cap-binding complex eIF4F. Other proteins are detected upon purification of the complex on cap-affinity columns. Among them is p20, a protein of unknown function encoded by the CAF20 gene. Here, we show a negative regulatory role for the p20 protein in translation initiation. Deletion of CAF20 partially suppresses mutations in translation initiation factors. Overexpression of the p20 protein results in a synthetic enhancement of translation mutation phenotypes. Similar effects are observed for mutations in the DED1 gene, which we have isolated as a multicopy suppressor of a temperature-sensitive eIF4E mutation. The DED1 gene encodes a putative RNA helicase of the DEAD-box family. The analyses of its suppressor activity, of polysome profiles of ded1 mutant strains, and of synthetic lethal interactions with different translation mutants indicate that the Ded1 protein has a role in translation initiation in S. cerevisiae.
Figures



References
-
- Merrick W C, Hershey J W B. In: Translational Control. Hershey J W B, Mathews M B, Sonenberg N, editors. Plainview, NY: Cold Spring Harbor Lab. Press; 1996. pp. 31–69.
-
- Iizuka N, Chen C, Yang Q, Johannes G, Sarnow P. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1995;203:155–177. - PubMed
-
- Jaramillo M, Browning K, Dever T E, Blum S, Trachsel H, Merrick W C, Ravel J M, Sonenberg N. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990;1050:134–139. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

