Homodimerization of the human interleukin 4 receptor alpha chain induces Cepsilon germline transcripts in B cells in the absence of the interleukin 2 receptor gamma chain
- PMID: 9159166
- PMCID: PMC20872
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.94.11.5866
Homodimerization of the human interleukin 4 receptor alpha chain induces Cepsilon germline transcripts in B cells in the absence of the interleukin 2 receptor gamma chain
Abstract
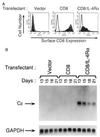
The cytokines interleukin (IL)-4 and IL-13 play a critical role in inducing Cepsilon germline transcripts and IgE isotype switching in human B cells. The IL-4 receptor (IL-4R) in B cells is composed of two chains, the IL-4-binding IL-4Ralpha chain, which is shared with the IL-13R, and the IL-2Rgamma (gammac) chain, which is shared with IL-7R, IL-9R, and IL-15R. IL-4 induces Cepsilon germline transcripts and IgE isotype switching in B cells from patients with gammac chain deficiency. Induction of Cepsilon germline transcripts by IL-4 in B cells that lack the gammac chain may involve signaling via the IL-13R. Alternatively, the IL-4Ralpha chain may transduce intracellular signals that lead to Cepsilon gene transcription independently of its association with other chains. We show that ligand-induced homodimerization of chimeric surface receptors consisting of the extracellular and transmembrane domains of the erythropoietin receptor and of the intracellular domain of IL-4Ralpha induces Janus kinase 1 (Jak1) activation, STAT6 activation, and Cepsilon germline transcripts in human B cell line BJAB. Disruption of the Jak1-binding proline-rich Box1 region of IL-4Ralpha abolished signaling by this chimeric receptor. Furthermore, B cells transfected with a chimeric CD8alpha/IL-4Ralpha receptor, which is expressed on the cell surface as a homodimer, constitutively expressed Cepsilon germline transcripts. These results suggest that homodimerization of the IL-4Ralpha chain is sufficient to transduce Jak1-dependent intracellular signals that lead to IgE isotype switching.
Figures




References
-
- Vercelli D, Geha R S. Curr Opin Immunol. 1992;4:794–797. - PubMed
-
- Zurawski S M, Chomarat P, Djossous O, Bidaud C, McKenzie P, Miossec A N J, Banchereau J, Zurawski G. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:13869–13878. - PubMed
-
- Kondo M, Takeshita T, Ishii N, Nakamura M, Watanabe S, Arai K, Sugamura K. Science. 1993;262:1874–1877. - PubMed
-
- De Saint Basile G, Di Santo J P, Fischer A. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1995;76:S165–S167. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

