Absence of peripheral blood T cell responses to "shared epitope' containing peptides in recent onset rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 9165996
- PMCID: PMC1752364
- DOI: 10.1136/ard.56.4.240
Absence of peripheral blood T cell responses to "shared epitope' containing peptides in recent onset rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
Objectives: To determine if peptides containing the 'shared epitope' sequence, QKRAA, from either endogenous, HLA-DR beta 1 (0401), or exogenous, Escherichia coli dnaJ, sources activate T cells in recent onset rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
Methods: Peripheral blood mononuclear cell (PBMC) proliferative and whole blood cytokine responses to shared epitope containing peptides from DR beta 1 (0401) and E coli dnaJ, to control peptides from DR beta 1 (0402) and hsp40 and to the recall antigen, tetanus toxoid, were tested in 20 untreated, recent onset RA subjects, 20 HLA, age, and sex matched healthy controls and 18 other subjects with inflammatory arthritis. PBMC proliferative responses to a second E coli dnaJ peptide (with the shared epitope at the N-terminus) and two peptides from type II collagen with high affinity for DR4(0401) were tested in a further 16 recent onset RA and 17 control subjects.
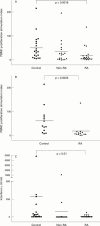
Results: PBMC proliferation and whole blood interferon gamma or interleukin 10 production in response to the shared epitope containing and control peptides were not different between the disease and control groups. On the other hand, compared with controls, RA subjects had significantly higher proliferation to a collagen II (aa 1307-1319) peptide, but significantly lower proliferation and interferon gamma production to tetanus toxoid.
Conclusion: Recent onset RA subjects had no demonstrable increase in peripheral blood T cell reactivity to shared epitope containing peptides. However, a proportion had increased T cell reactivity to a peptide of similar length from a candidate RA autoantigen, collagen type II. Their impaired responses to tetanus are in keeping with evidence for general T cell hyporesponsiveness in RA.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Interferon-gamma production in response to in vitro stimulation with collagen type II in rheumatoid arthritis is associated with HLA-DRB1(*)0401 and HLA-DQ8.Arthritis Res. 2000;2(1):75-84. doi: 10.1186/ar71. Arthritis Res. 2000. PMID: 11219392 Free PMC article.
-
Collagen Specific T-Cell Repertoire and HLA-DR Alleles: Biomarkers of Active Refractory Rheumatoid Arthritis.EBioMedicine. 2015 Nov 17;2(12):2037-45. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2015.11.019. eCollection 2015 Dec. EBioMedicine. 2015. PMID: 26844284 Free PMC article.
-
The susceptibility sequence to rheumatoid arthritis is a cross-reactive B cell epitope shared by the Escherichia coli heat shock protein dnaJ and the histocompatibility leukocyte antigen DRB10401 molecule.J Clin Invest. 1992 Jan;89(1):327-31. doi: 10.1172/JCI115580. J Clin Invest. 1992. PMID: 1370300 Free PMC article.
-
HLA-DRB1 motifs and heat shock proteins in rheumatoid arthritis.Int Rev Immunol. 1998;17(5-6):263-71. doi: 10.3109/08830189809054405. Int Rev Immunol. 1998. PMID: 10036634 Review.
-
Molecular basis for the association between HLA DR4 and rheumatoid arthritis. From the shared epitope hypothesis to a peptidic model of rheumatoid arthritis.Clin Biochem. 1992 Jun;25(3):209-12. doi: 10.1016/0009-9120(92)90328-p. Clin Biochem. 1992. PMID: 1378777 Review.
Cited by
-
Hsp40 proteins modulate humoral and cellular immune response in rheumatoid arthritis patients.Cell Stress Chaperones. 2010 Sep;15(5):555-66. doi: 10.1007/s12192-010-0168-z. Epub 2010 Feb 2. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2010. PMID: 20127215 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

